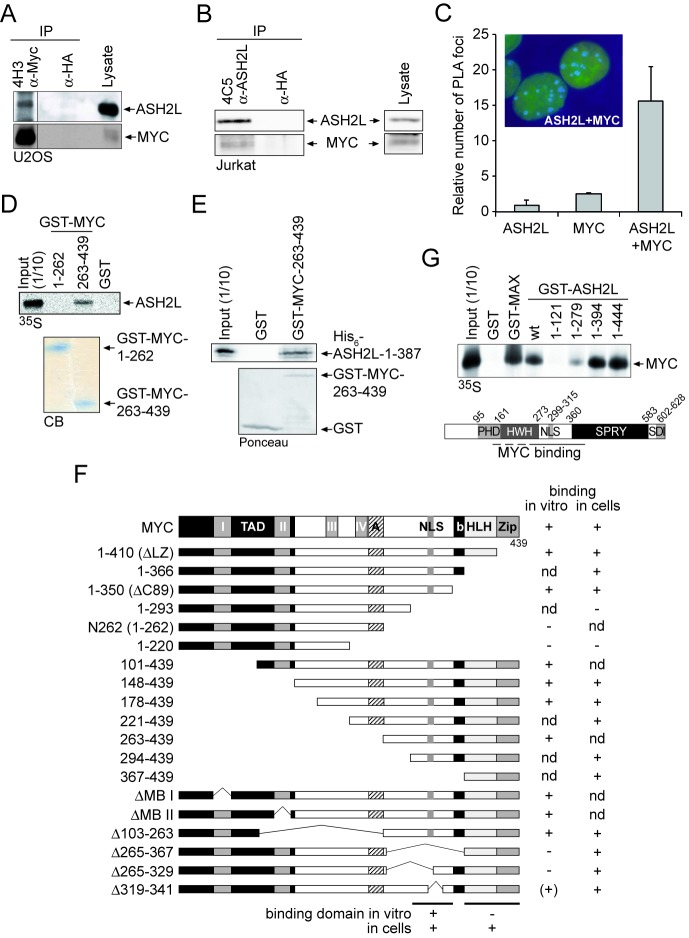
Figure 1.
ASH2L interacts with MYC in vitro and in cells. (A) MYC was immunoprecipitated from U2OS cells using the mAb 4H3. HA-tag-specific antibodies served as control. The co-immunoprecipitation of ASH2L was analyzed by immunoblotting using the ASH2L-specific 4C5 mAb. MYC was detected using pAb N262. The different lanes were run on the same western blot. (B) ASH2L was immunoprecipitated from lysates of Jurkat T cells using the mAb 4C5. ASH2L was detected on western blots with pAb 548 and the co-immunoprecipitated MYC with MYC-specific N262 polyclonal antibodies. Antibodies specific for the HA-tag were used as negative control. (C) In situ PLA in U2OS cells using primary mAb 4C5 to detect ASH2L and primary N262 purified pAb to detect MYC and species-specific secondary antibodies with oligos attached to them (PLA probes). For negative control, one primary antibody was assayed with the species-specific secondary antibody. The number of foci were counted from 50 cells of three independent experiments, displayed as mean value and standard deviation (using students’ t-test). The inset shows two representative cells with foci in blue and the DNA stained in green. (D) GST-pull-down assays were carried out with different fragments of MYC (as indicated) fused to GST and GST alone as control. The binding of in vitro transcribed and translated, 35S-methionine-labeled ASH2L was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The fusion proteins used are shown below in a Coomassie-Blue-stained gel (CB). (E) GST-pull-down assay of bacterially expressed and purified MYC and ASH2L fusion proteins were performed with GST-MYC-C176 containing the ASH2L interaction domain and with His6-ASH2L-N387 containing the N-terminal 387 amino acids that are sufficient for the interaction with MYC. (F) Summary of the interactions of ASH2L with MYC of in vitro pull-down assays and of co-immunoprecipitation experiments obtained from HEK293 cells upon transient expression of the respective fragments. (G) GST-pull-down assays were carried out with different fragments of ASH2L (as indicated) fused to GST and GST alone as control. The binding of in vitro transcribed and translated, 35S-methionine-labeled MYC was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The bottom panel shows the schematic organization of ASH2L. PHD, atypical plant homeodomain; HWH, helix-winged-helix domain; NLS, nuclear localization signal; SPRY, an SP1a and RYanodine receptor domain; SDI, SDC1/DPY30 interaction motif (54,114–116). The results of the GST-pull-down assays are summarized schematically at the bottom.