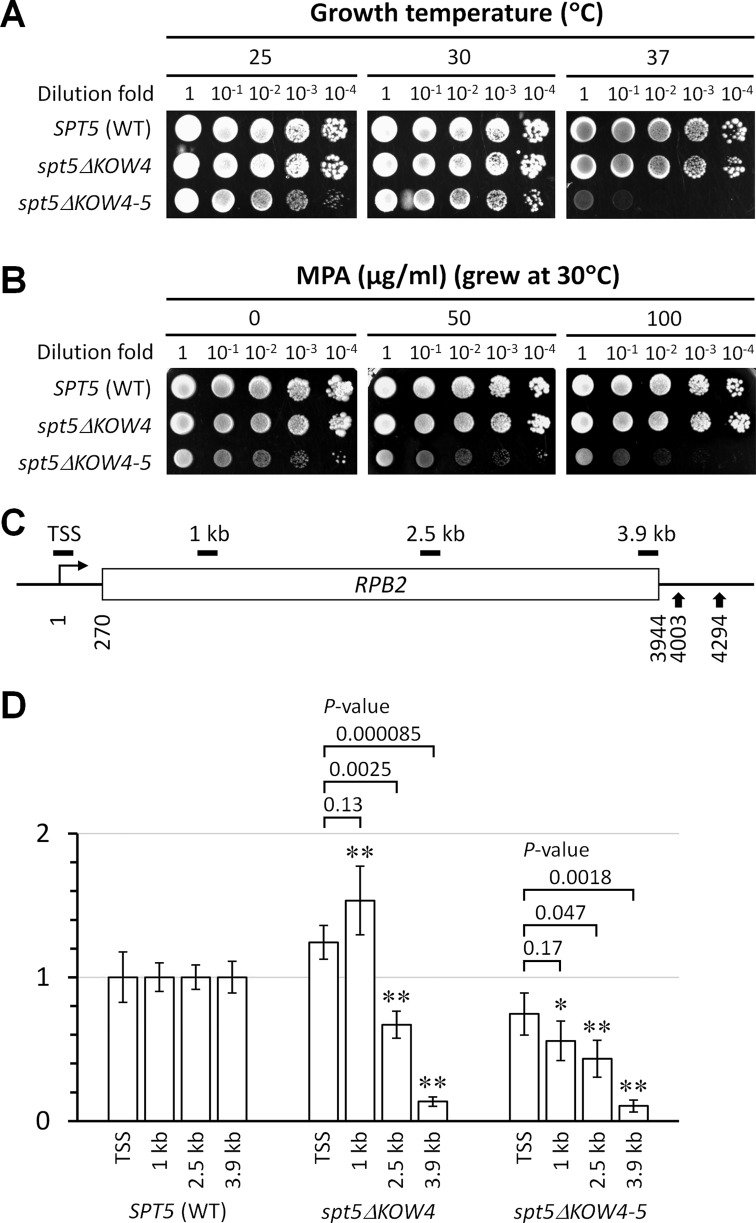
Figure 5.
Deletion of Spt5 KOW4-5 causes defects in transcription elongation. (A) Growth of yeast cells expressing wild type (WT), KOW4 deleted (spt5ΔKOW4) and KOW4-5 deleted (spt5ΔKOW4-5) Spt5 at different temperatures. (B) Growth of the different yeast strains in the presence of different concentrations of mycophenolic acid (MPA), a nucleotide depletion drug. (C) Schematic of the RPB2 gene. Nucleotide positions are relative to the transcription start site (TSS). Vertical arrows at the 3′ end of the gene indicate the two alternative polyadenylation sites (48). Short horizontal bars above the schematic indicate regions of 134–150 bp amplified by real-time PCR for quantification of ChIP fragments of the RPB2 gene (see Supplementary Table S3). (D) RNAP II densities in different regions of the RPB2 gene. The RNAP II densities in the TSS, 1 kb, 2.5 kb and 3.9 kb regions of the RPB2 gene in WT cells were normalized to 1. The RNAP II densities in the different regions of the RPB2 gene in spt5ΔKOW4 and spt5ΔKOW4-5 cells are relative to those in the corresponding regions of the RPB2 gene in WT cells. The values of RNAP II densities are represented as mean (+/− S.D.) of three ChIP experiments. Single asterisk (*) and double asterisks (**) denote a P-value of <0.05 and <0.01, respectively, in the Student's t-test between the mutant and WT cells for RNAP II densities in the corresponding regions of the RPB2 gene. The RNAP II densities in the TSS region of the RPB2 gene in spt5ΔKOW4 and spt5ΔKOW4-5 cells were not significantly different from that in the WT cells (P-values are 0.1 and 0.3 for the spt5ΔKOW4 and spt5ΔKOW4-5 cells, respectively; a P-value of <0.05 is considered to be significant). Above the bars of spt5ΔKOW4 and spt5ΔKOW4-5 samples are shown the P-values of Student's t-test between the TSS region and the 1, 2.5 or 3.9 kb region.