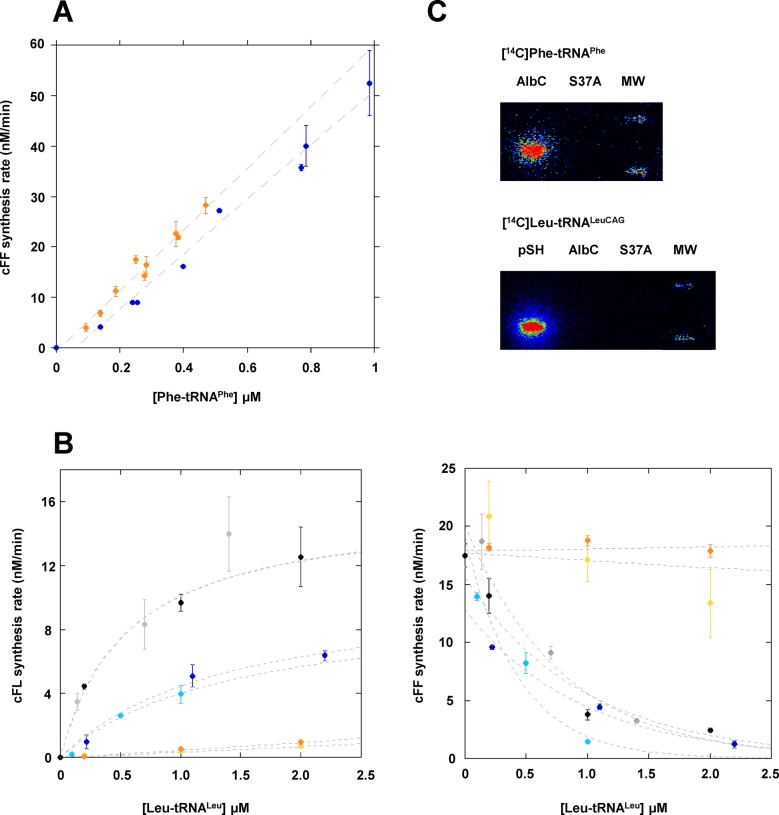
Figure 1.
(A) cFF-synthesizing activity of AlbC using either tRNAPhe purified from E. coli (blue) or tRNAPhe obtained by in vitro transcription (orange). Enzymatic measurements were performed as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ with 50 nM AlbC. The points reported are the result of three independent experiments. Error bars show the uncertainty on measurement. (B) Rate of formation of cFL (left panel) or cFF (right panel) by AlbC for different tRNALeu isoacceptors. Kinetics of synthesis were determined with 0.2 μM Phe-tRNAPhe and three concentrations of Leu-tRNALeu. Isoacceptors are identified by the following colours: tRNALeuCAA (light blue), tRNALeuTAG (dark blue), tRNALeuGAG (yellow), tRNALeuTAA (orange), tRNALeuCAG* (grey), tRNALeuCAG (black). Curves are drawn for clarity and are not representative of kinetic models. (C) Covalent labelling of AlbC, S37A and pSHaeC06 (pSH) by [14C]Phe transferred from [14C]Phe-tRNAPhe or [14C]Leu transferred from [14C]Leu-tRNALeuCAG. Enzymes were incubated with labelled aa-tRNA, as described in ‘Materials and Methods’, separated on SDS-PAGE, then transferred onto a PVDF membrane that was analysed with a radioimager.