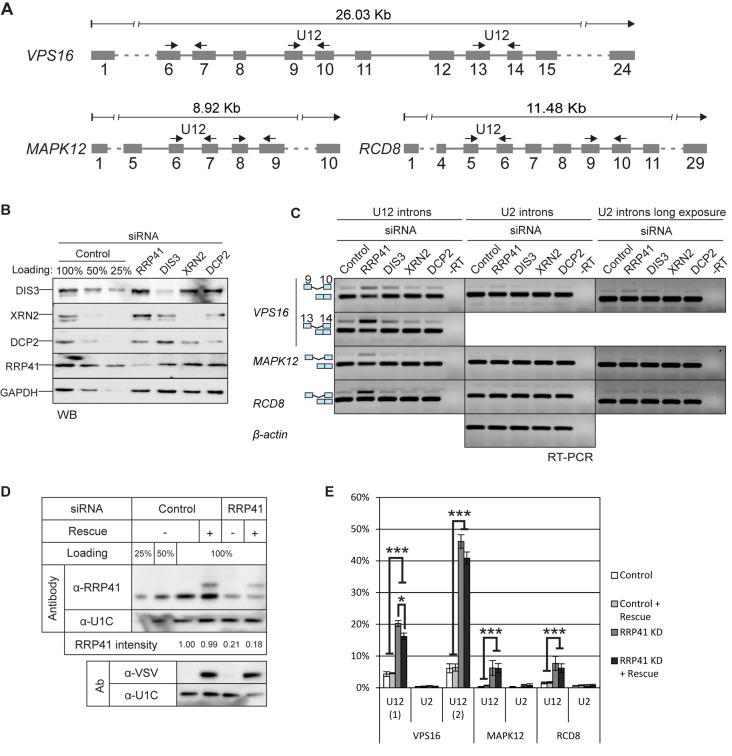
Figure 1.
U12-intron-containing transcripts are stabilized by the exosome knockdown. (A) Exon/intron structures of human VPS16, MAPK12 and RCD8 genes and positions of the primers used in RT-PCR experiments (arrows). (B) Western blot illustrating the depletion of RRP41, DIS3, XRN2 and DCP2 upon siRNA-mediated knockdown. Cell lysates from cells treated with control siRNA were loaded in the indicated amounts. (C) RT-PCR analysis of the three transcripts described in panel (A) and beta-actin after knockdown of RRP41, DIS3, XRN2 or DCP2. The positions of the transcripts (i.e. mRNA versus pre-mRNA) are indicated on the left. U2 panels are shown in two versions, in the middle panel contrast settings are the same as in the U12 panel; in the rightmost panel the same gel is shown with darker settings to reveal the weak U2 intron signals. (D) Expression level of VSV-epitope-tagged RRP41 containing silent mutations at the siRNA target site, analyzed by western blotting using a polyclonal anti-RRP41 antibody and anti-VSV tag antibody. The relative intensity of the endogenous RRP41 signal (normalized to U1C signal) is shown below the panels. (E) Quantification of intron retention levels upon RRP41 knockdown and with or without RRP41 rescue. VPS16, MAPK12 and RCD8 spliced and unspliced signals in agarose gels containing separated RT-PCR products were quantified (*P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 with Student's t-test).