Figure 1.
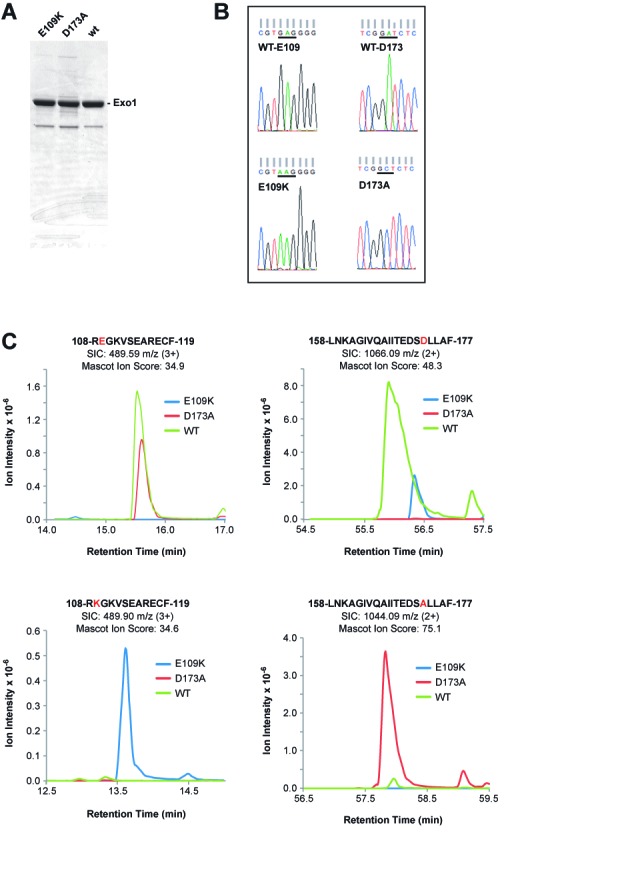
Purity and sequence confirmation of Exo1 and Exo1 variants used in this study. (A) Samples (5 μg) of Exo1 preparations used in this study were subjected to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. (B) Lysates of baculovirus-infected SF9 cells employed for protein isolation were used as sources of template DNA for PCR amplification of the N-terminal 341 codons of Exo1. DNA sequence analysis of PCR products demonstrated presence of Glu and Asp codons at positions 109 and 173 for wild type Exo1 (upper reads); Lys at position 109 for Exo1-E109K (lower left read) and Ala at position 173 for Exo1-D173A (lower right read). (C) EIC peak traces of chymotryptic products spanning residues E109 and D173 across three LC-MS injections. Each EIC was performed ±20 ppm around the monoisotopic precursor m/z. Peaks were manually verified using retention time relative to qualitative peptide identification time as well as predicted ratio of C12 and C13 isotopomer peaks.
