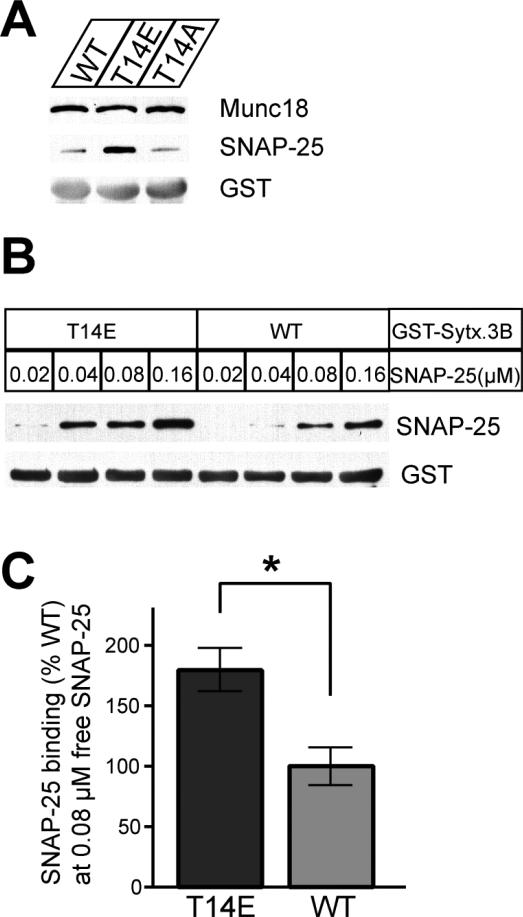
Figure 8. A phosphomimetic mutation of syntaxin 3B (T14E) increases the binding affinity to SNAP25.
A. GST pulldown assays with retina extract were used to investigate the binding of SNAP-25 and Munc18 to wildtype GST-syntaxin 3B (WT), a phosphomimetic mutant (T14E) and a control mutant (T14A). The pulldown samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against Munc18, SNAP-25 and GST. The phosphomimetic T14E mutant protein had a much higher affinity to SNAP-25 than the wildtype or the T14A mutant protein but Munc18 was bound with similar efficiency by all three proteins. B. GST pulldown experiments were performed to directly test the binding of recombinant SNAP-25 to wildtype (WT) or mutant (T14E) GST-syntaxin 3B. The concentration of SNAP-25 in the assay is given above the lanes. The phosphomimetic T14E mutant protein bound recombinant SNAP-25 with a higher affinity than GST-syntaxin 3B. C. Multiple pulldown experiments were performed using recombinant SNAP-25 (0.08 μM) and the amount of bound SNAP-25 was quantified. Results were normalized to the amount bound by the wildtype protein. The T14E mutant protein showed a significantly higher affinity for recombinant SNAP-25 than the wild type protein. (WT: 100.0 ± 15.97%; T14E: 179.5 ± 18.63% (+/- SEM, n=3, p-value= 0.0317 (unpaired two tailed t test)).