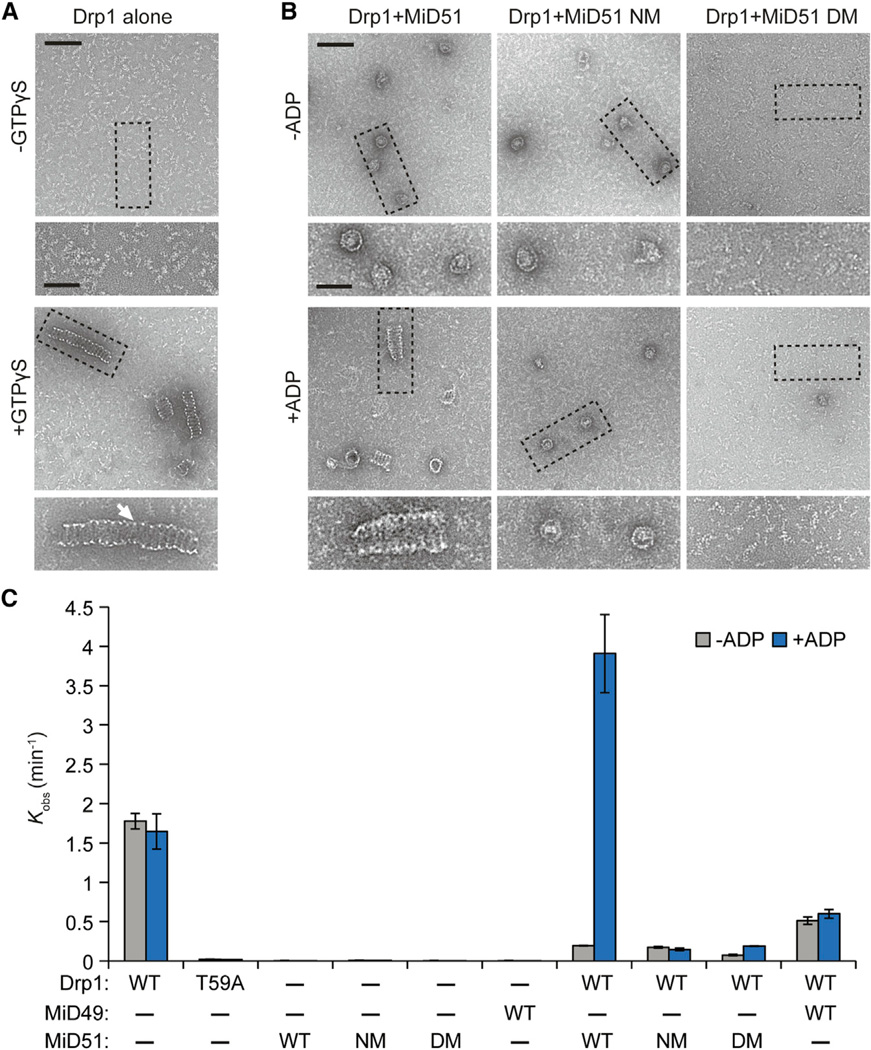
Figure 7. MiD51 and ADP Promote Drp1 Spiral Assembly and GTP Hydrolysis.
(A and B) Negative stain transmission electron microscopy of Drp1 oligomers. Images are representative of three independent experiments. (A) Recombinant mouse Drp1 forms regular spiral-tubular structures in the presence of a nonhydrolyzable analog of GTP, GTPγS. White arrow highlights the thin edge of spiral-tubular structures. (B) Effects on Drp1 spiral-tubular formation upon addition of MiD51 proteins with and without ADP. GTPγS was present in all reactions. Dashed boxes indicate inset boundaries. Scale bar, 100 nm; inset scale bar, 50 nm.
(C) Effect of MiD51 and ADP on GTP hydrolysis by Drp1. Initial GTP hydrolysis rates were measured with the indicated proteins, with or without ADP. Reactions were performed at saturating GTP (1 mM) with 150 mM NaCl. NM, nucleotide-binding site mutant (S189A); DM, compound dimer mutant. T59A is a Drp1 catalytic mutant. Results are the average of three independent experiments ±SD.