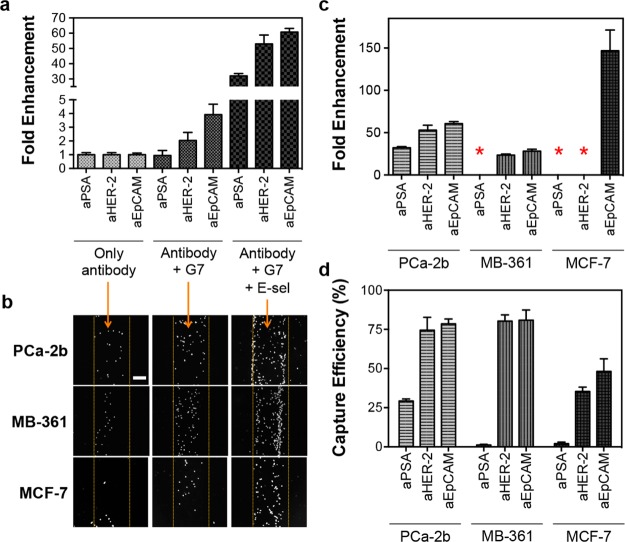
Figure 2.
Enhanced capture efficiencies of the multifunctional surfaces by the combined effect of cell rolling and multivalent binding. (a) Fold enhancement in capture efficiency of the surface functionalized with the three antibodies, measured using MDA-PCa-2b cells. The surface with E-selectin and G7 PAMAM dendrimers shows substantially enhanced capture efficiencies up to 60-fold, compared to the surface with antibodies only. (b) Bright field microscopic images of the captured MDA-PCa-2b, MDA-MB-361, and MCF-7 cells on the surfaces functionalized with aEpCAM. The numbers of the captured cells clearly increase with addition of the dendrimers and E-selectin without an increase of nonspecific capture (Scale bar = 200 μm). (c) Fold increase in capture efficiencies of the surfaces with the three antibodies, G7 PAMAM dendrimers, and E-selectin, compared to the surfaces functionalized with the antibodies alone. The three cancer cell lines, depending on their surface marker expressions, all demonstrate enhanced capture efficiencies on the multifunctional surfaces, as high as 150 fold. (d) Quantitative capture efficiencies of each of the antibodies on the multifunctional surface toward various cancer cells. Although there is a degree of variations, the surface marker-dependent capturing achieves up to 81% capture efficiency. *No fold enhancements because of negligible binding without E-selectin. The Error bars: standard error (n = 4).