Figure 4. Meiotic germ cells are required for precocious pregranulosa cell differentiation.
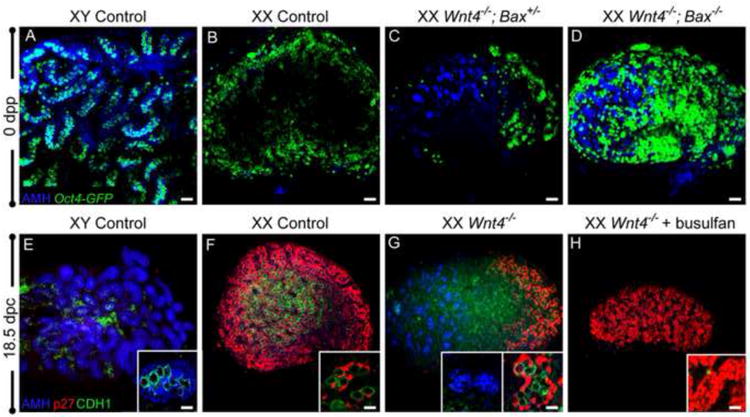
(A-D) At birth (0 days post-partum, dpp), gonads were immunostained for AMH (blue), and germ cells were visualized with Oct4-Gfp (green) to determine whether rescue of germ cells in agametic ovarian regions blocked AMH activation. AMH is expressed in Sertoli cells (A) and not in control ovaries (B). XX Wnt4-/-; Bax+/- mutants phenocopied XX Wnt4-/- mutants, with ectopic activation of AMH in agametic regions (C). In double mutant Wnt4-/-; Bax-/- ovaries, rescued germ cells were present throughout the ovary, but did not prevent ectopic activation of AMH at the anterior end of the ovary (D). (E-H) To determine whether the absence of germ cells blocked or exacerbated ectopic AMH expression, germ cells were depleted by injection of busulfan at 11.5 dpc. As expected, male and female control gonads expressed AMH (blue) and p27 (red), respectively (E,F). Wnt4-/- ovaries had ectopic AMH at the anterior end and p27 expression at the posterior end, surrounding CDH1-positive germ cells (green) (G). Following busulfan treatment, XX Wnt4-/- ovaries did not ectopically activate AMH, and all pregranulosa cells, at both the anterior and posterior ends, maintained expression of p27 (H). Whole mount immunostaining was performed for all samples. For the samples in (A) and (E), a small piece of testis was used as a control for whole mount antibody immunostaining. Scale bars represent 50 μm in main panels and 10 μm in all insets.
