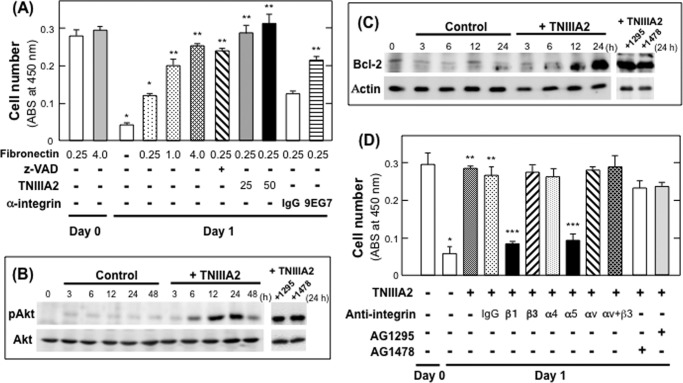
FIGURE 1.
Protection of NIH3T3 cells from serum deprivation-dependent apoptosis by TNIIIA2. A, NIH3T3 cells were seeded on a plate coated with the indicated concentration (μg/ml) of fibronectin and allowed to adhere. After completion of adhesion to the fibronectin substrate, cells were cultured with serum-free medium in the presence or absence of anti-apoptotic reagent, benzyloxycarbonyl-VAD (z-VAD; 50 μm), TNIIIA2 (25 or 50 μg/ml), normal IgG, or β1-integrin-activating mAb 9EG7 (20 μg/ml) for 1 day, and WST assays were conducted to detect viable cells. Each point represents the mean ± S.D. of triplicate determinations. One of three individual experiments is shown. *, p < 0.005 versus untreated cells on fibronectin (0.25 μg/ml) on day 0. **, p < 0.01 versus untreated cells on fibronectin (0.25 μg/ml) on day 1. B and C, NIH3T3 cells were cultured with serum-free medium in the presence or absence of TNIIIA2 (25 μg/ml) and in the presence or absence of tyrosine kinase inhibitor for PDGF receptor (AG1295, represented by 1295) or EGF-receptor (AG1478, represented by 1478). After the indicated period, cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis to detect Akt phosphorylation (B) and Bcl-2 expression (C). D, cells adhering to the fibronectin were cultured with serum-free medium with or without TNIIIA2 in the presence or absence of normal IgG or anti-integrin function-blocking mAb (15 μg IgG/ml) directed to β1, β3, α4, α5, αv subunit, or a mixture of anti-αv and β3 (represented by αv+β3). Each point represents the mean ± S.D. of triplicate determinations. One of three individual experiments is shown. *, p < 0.005 versus untreated on day 0. **, p < 0.005 versus untreated on day 1. ***, p < 0.005 versus treated with normal IgG.