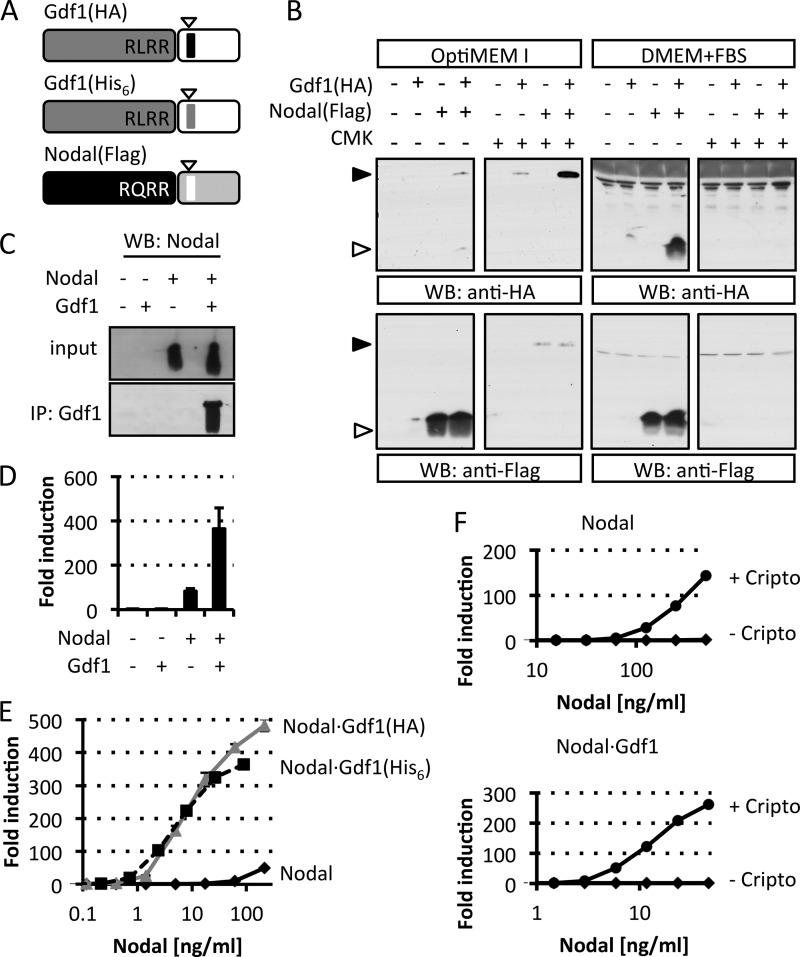
FIGURE 1.
Dependence of extracellular Gdf1 on Nodal. A, schematic depiction of HA-, His6-, or FLAG-tagged Gdf1 and Nodal precursors. The epitopes (arrowheads) were inserted 4 residues after the precursor cleavage sites RLRR and RQRR. N-terminal prodomains are shaded dark gray or black. B, Western blot (WB) analysis of media conditioned by HEK293T cell lines that were stably transduced with Gdf1, Nodal, or both. Where specified, cells were treated with 10 μm decanoyl-RRKR-chloromethyl ketone (CMK) during medium conditioning. Opti-MEM I and DMEM samples were analyzed separately on different blots with distinct exposure times in this experiment. C, Western blot analysis of Nodal following immunoprecipitation (IP) of Gdf1(HA) from complete conditioned media (DMEM+FBS). D, induction of the Smad3 luciferase reporter CAGA-luc in stable H-CrCR reporter cells by serum-containing conditioned DMEM. Gdf1 is HA-tagged. E, induction of CAGA-luc by serum-containing Nodal (black, solid line), Nodal·Gdf1(HA) (gray, solid line), or Nodal·Gdf1(His6) (black, dashed line) conditioned media. HA-tagged Gdf1 and His6-tagged Gdf1 similarly potentiate Nodal activity. HA reacted more strongly than His6 in Western blots, but His6 was later preferred for affinity purification. F, induction of CAGA-luc by recombinant Nodal or Nodal·Gdf1(His6) in naïve (diamonds) or Cripto-overexpressing (circles) reporter cells. Note that concentrations in E and F only refer to total amounts of Nodal because tagged Gdf1 was not quantified. In D, E, and F, error bars represent S.D.