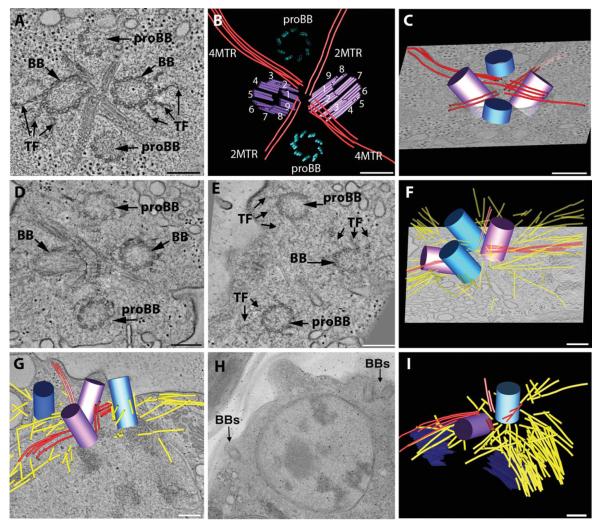
Fig. 1. Early events in basal body duplication in Chlamydomonas.
(A, B, C) Interphase cells contain a basal body complex formed from two mature (BB) and two immature basal bodies (proBB) (purple and blue, respectively) separated by four bundles of rootlet MTs in a cross-like arrangement (red lines). A movie of the complete tomographic volume is shown in Supporting Information movie S1. (D, E, F) Cell cultures were synchronized using cycles of light and dark and examined by electron tomography. Soon after entering the dark cycle, the probasal bodies elongate (blue cylinders), the rootlet MTs remain intact (red lines) and there is an increase in cytoplasmic MTs (yellow lines). The elongated probasal bodies (proBB) assemble TF similar to the mature basal bodies (BB). A movie of the complete tomographic volume is shown in Supporting Information movie S2. (G, H, I) At late prophase, the basal body complex separates and two basal bodies migrate to opposite sides of the nucleus (BBs) and there is a noticeable increase in cytoplasmic MTs (yellow lines). Bar = 200 nm.