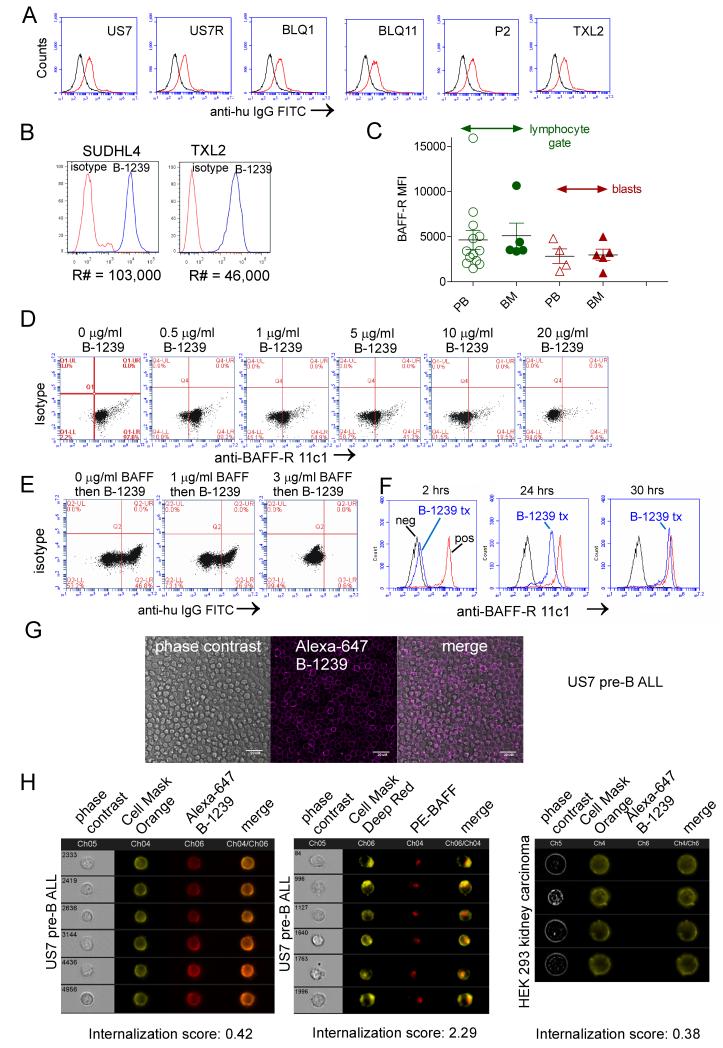
Figure 2.
Binding of humanized mAb B-1239 to the BAFF-R. A, Antibody binding of B-1239 (10 μg/ml, 2 hrs) α-BAFF-R antibody to the indicated patient-derived ALL cells detected using FITC anti-human IgG. Black histograms, control anti-human IgG; grey histograms, cells first incubated with B-1239, then stained with anti-human IgG antibody. B, Comparative analysis for BAFF-R copy number (R#) on the surface of SUDHL4 (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma) and Ph-positive ALL TXL2 as measured by B-1239. C, Comparison of mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) for BAFF-R expression on CD19+, BAFF-R+ residual normal B-lineage cells and CD19+, BAFF-R+ blasts for 4-9 different patient samples. Normal non-B lymphocytes did not express the BAFF-R. D, Binding of PE-labeled anti-BAFF-R antibody 11c1 clone (BD Biosciences) to human US7 ALL cells after pre-incubation with the indicated amounts of B-1239. E, Ability of recombinant BAFF to inhibit binding of 5 mg/ml B-1239 to the BAFF-R on US7 ALL cells as detected with FITC anti-human IgG antibody. F, Cell surface detection as measured by competition of PE-labeled anti-BAFF-R 11c1 antibodies with unlabeled B-1239 mAb on US7 pre-B ALL cells after addition of 30 μg/ml antibody on t =0. Control, unstained cells; blue, cells treated with B-1239. Red, no B-1239 added. G, Localization of Alexa-647-conjugated B-1239 antibodies using confocal microscopy. Bar, 20 μm. H, Representative Amnis ImageStream images showing specific cell surface attachment and lack of internalization of Alexa-627 B-1239 to US7 pre-B ALL cells, compared to positive control internalization of PE-anti-BAFF antibodies, and negative binding control for Alexa-647 B-1239 to HEK 293 cells which lack BAFF-R expression.