Figure 2. Characterisation of XY Fgfr2hob/hob embryonic gonad development on the C57BL/6J (B6) background and complementation test with the Fgfr2tm1.1Dor null allele.
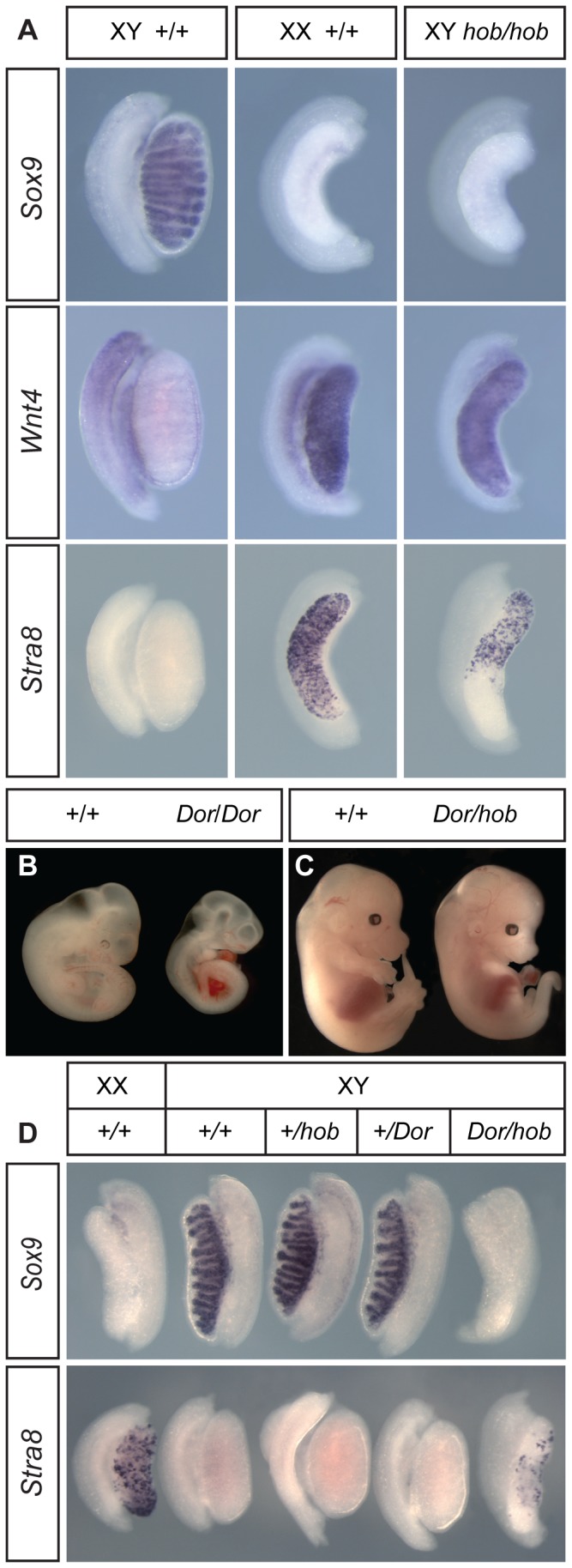
A) WMISH analysis of gonads at 14.5 dpc from XY wild-type, XX wild-type and XY Fgfr2hob/hob embryos using a marker of the Sertoli cell lineage (Sox9), ovarian somatic cells (Wnt4) and meiotic germ cells (Stra8). B) Embryos homozygous for the Fgfr2tm1.1Dor allele (Dor/Dor) are much smaller than wild-type controls (+/+) at 11.5 dpc and also lack limbs. C) Embryos at 14.5 dpc doubly heterozygous for the Fgfr2hob and Fgfr2tm1.1Dor alleles (Dor/hob) lack limbs and are noticeably smaller than wild-type controls (+/+). D) Upper panel: Sox9 WMISH of 13.5 dpc embryonic gonads from control and XY Fgfr2tm1.1Dor/hob doubly heterozygous embryos; lower panel: Stra8 WMISH of 14.5 gonads from embryos of same genotypes as upper panel. The developmental stage of the doubly heterozygous gonad in the lower panel appears significantly retarded when compared to the XX control.
