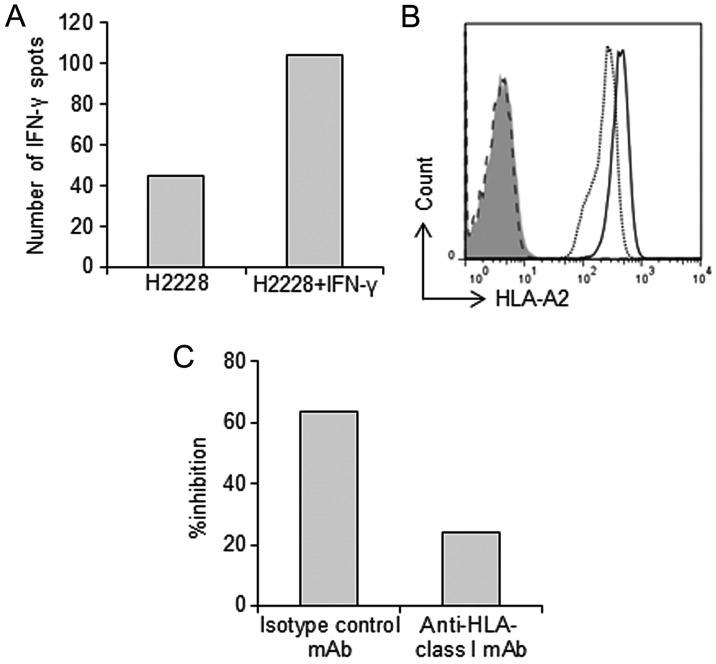
Figure 4.
Recognition of lung carcinoma cells expressing HLA-A*02:01 and the EML4-ALK fusion gene by the peptide A-specific CTL clone. The peptide A-specific CTL clone recognized H2228 cells pretreated with IFN-γ 48 h prior to the assay. (A) The peptide A-specific CTL clone (1×104 cells) was incubated with H2228 cells with or without IFN-γ. IFN-γ production was detected by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. (B) IFN-γ increased expression of HLA-A2 presented on H2228 cells. Incubation of H2228 cells with 100 U/ml IFN-γ for 48 h increased HLA-A2 presentation on the cells. Dotted line, HLA-A2 on H2228 cells without IFN-γ. Black line, HLA-A2 on H2228 cells incubated with IFN-γ (higher than on H2228 cells without IFN-γ). Dashed line and shaded region: no staining of H2228 cells with/without IFN-γ. (C) Inhibition of IFN-γ production by an anti-HLA-class I mAb. Blocking experiments were performed using an HLA-A, -B, -C-specific mAb (W6/32) or an isotype control mAb (mIgG2a,κ). The peptide A-specific CTL clone was incubated with H2228 cells (HLA-A*02:01+/EML4-ALK+) pretreated with IFN-γ 48 h prior to examination. IFN-γ-producing CTL clones were detected by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. The bar graph shows the percentage of inhibition. CTL, cytotoxic T cell.