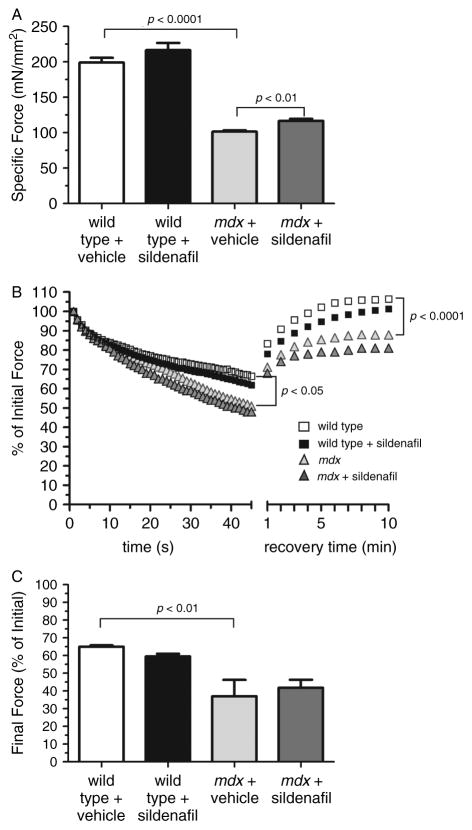
Figure 1.
Sildenafil increases mdx diaphragm muscle specific force output. (A) Maximal specific force output of wild-type and mdx diaphragm strips treated with vehicle or sildenafil. Treated mdx mice were significantly stronger than untreated mdx controls. (B) Representative traces of fatigue resistance profiles of wild-type and mdx diaphragms treated with vehicle or sildenafil. Mdx muscles exhibited significant muscle fatigue compared with wild-type controls, with force deficits during repetitive stimulation and recovery phases (marked post-exercise weakness). Sildenafil treatment did not impact the fatigue resistance of wild-type or mdx diaphragm muscle. p < 0.05 refers to the difference in force output of untreated wild-type and untreated mdx diaphragms during repetitive stimulation. p < 0.0001 refers to the difference in force output of untreated wild-type and untreated mdx diaphragms during the recovery phase. (C) Mean final force output at the end of the repetitive stimulation phase in wild-type and mdx diaphragm strips treated with vehicle or sildenafil of a fatigue protocol. Mdx muscles show a significant force deficit at the end of repetitive stimulation compared with wild-type. Sildenafil has no impact on the final force output in wild-type or mdx diaphragms. Wild-type untreated and sildenafil-treated: n = 5 each. mdx untreated and sildenafil-treated: n = 5 and 9, respectively.