Figure One.
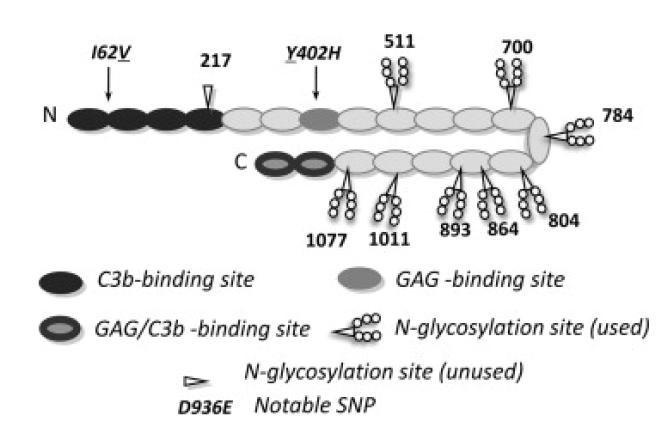
Summary of complement factor H structure and binding sites. Cartoon of human FH (SwissProt ID P08603) molecule that may have a bent-back overall architecture [72]. Each of 20 CCP modules (ovals) contains ~60 amino acid residues, is β-strand rich, and has two disulphide bonds. Positions of notable SNPs (see text) are indicated – underlines denote the variant produced in this study. Shading signifies binding sites for C3b and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) (or both in the case of CCP modules 19 and 20 that also bind to sialic acid). Eight of nine potential N-glycosylation sites are occupied (as indicated) in the native protein – P. pastoris-derived glycans were enzymatically cleaved during preparation of recombinant (r)FH. The eight asparagine residues were mutated to glutamine residues in the “All-Q” mutant.