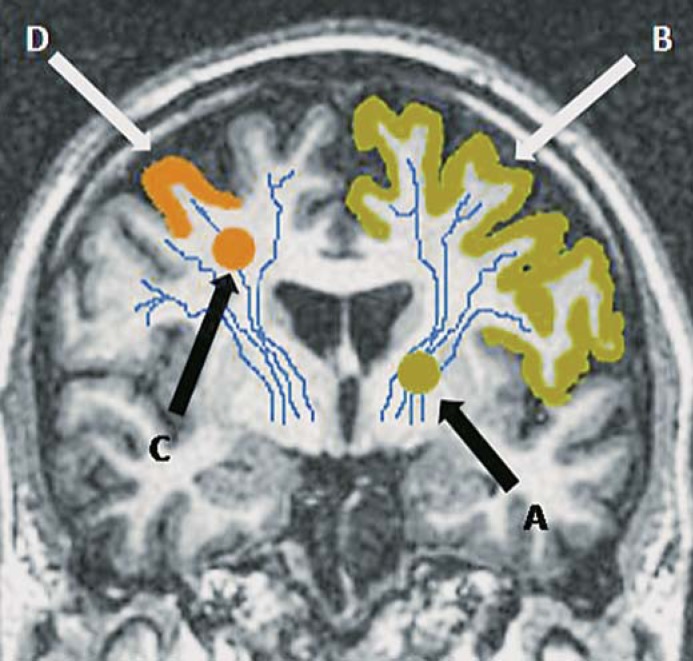
Fig. 1.
Coronal T1-weighted MRI brain to demonstrate how the site of a small subcortical (lacunar) infarct could influence clinical presentation. A small subcortical infarct lying in the left internal capsule, i.e. deep white matter (A), would cause functional disconnection of a large area of cortex (B, shaded). A peripheral small subcortical infarct lying close to cortex (C) would affect only a limited area of cortex (D, shaded), and could mimic a mild cortical stroke.