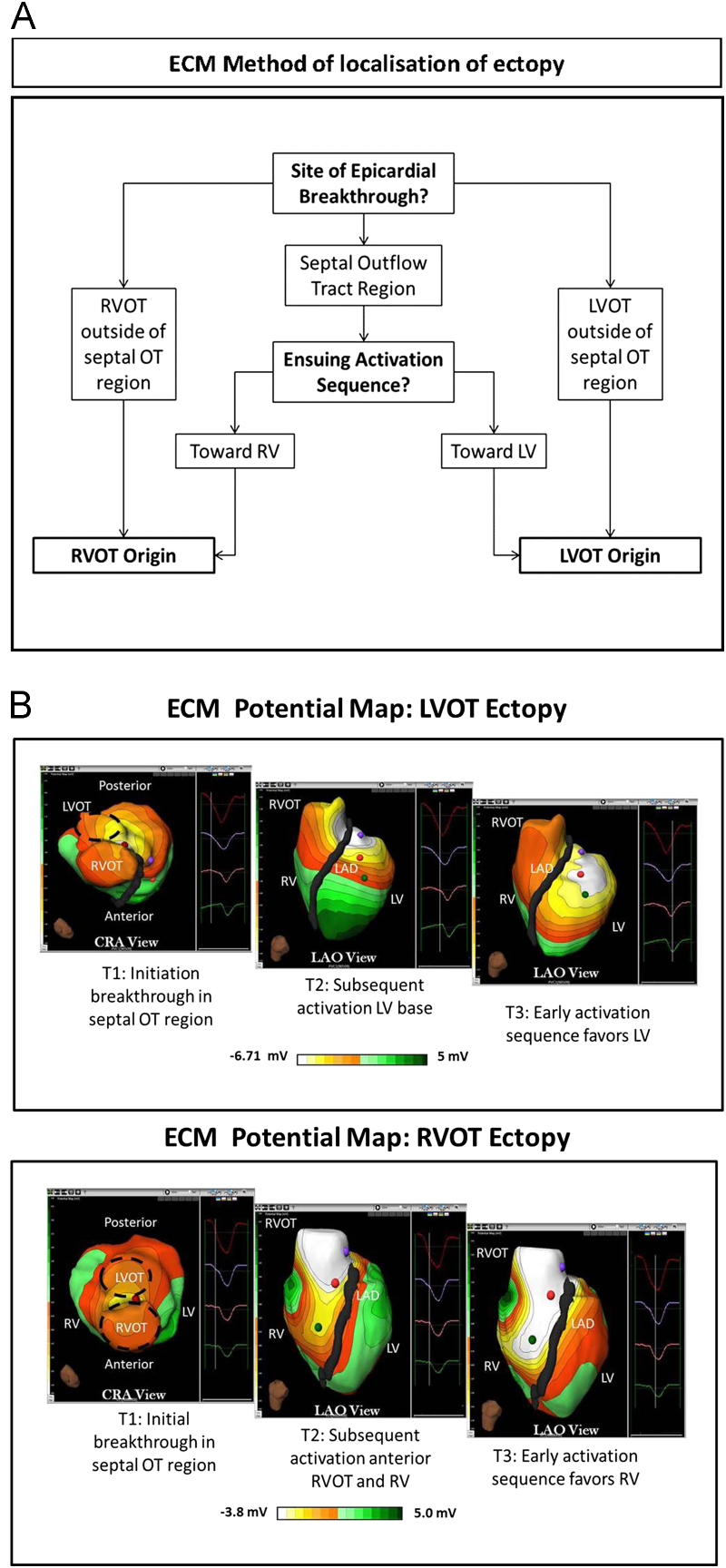
Figure 1.
A: ECM method of localization of ectopy origin. B: ECM potential maps of RVOT and LVOT ectopy. The images show the ECM potential PVC map from the cranial and LAO views at 3 time points: T1, initiation of epicardial breakthrough, and 2 later time points (T2 and T3). Top: After epicardial breakout in the septal groove, the ensuing activation spreads directly anteriorly toward the RV, suggesting RVOT origin. The successful ablation site here was in the mid-septal RVOT. Bottom: After epicardial breakout in the septal groove, the ensuing activation spreads posteriorly toward the LV, favoring the left ventricle. The successful ablation site here was in the anterolateral LVOT. CRA = cranial; ECM = electrocardiographic mapping; LAD = left anterior descending; LAO = left anterior oblique; LV = left ventricle; LVOT = left ventricular outflow tract; PVC = premature ventricular complex; OT = outflow tract; RV = right ventricle; RVOT = right ventricular outflow tract.