Fig. 3.
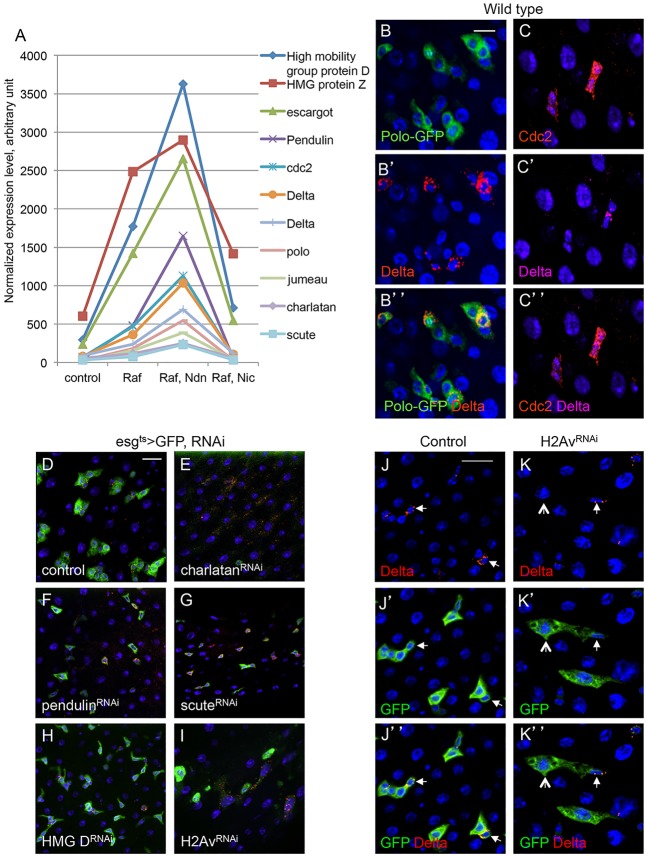
Expression and function of representative genes associated with ISCs or precursors. (A) The plot shows normalized expression of selected genes from SOM clusters c4, c5 and c8, in which the well-known ISC/precursor cell markers Delta and escargot are included. Average values from the four microarray experiments are shown. Genes in this set have diverse molecular functions. (B-C″) Expression analysis of the cell-cycle regulators Polo and Cdc2 in wild-type midguts. The Polo-GFP is a FlyTrap line in which the GFP-coding sequence is fused with the endogenous Polo-coding sequence. The expression was detected by anti-GFP immunofluorescence staining. The Polo-GFP was detected in Delta+ cells and neighboring EBs. Cdc2 antibody staining for the endogenous protein was similarly present in both Delta+ ISCs and adjacent EBs. (D-I) Functional analysis by RNAi of potential ISC regulators. Transgenic RNAi flies for chn, pendulin, scute, HMG D and H2Av were crossed with esgts>GFP. Control was a cross with w– flies. Adult flies ∼5 days old were placed at 29°C for 3 days more and the midguts were dissected for imaging. (J-K″) H2Av RNAi midguts stained for Delta expression showing that ISCs still had Delta expression (arrows), but GFP+ cell nests had lower cell numbers and the neighboring EB appeared to be larger in size (arrowheads in K).