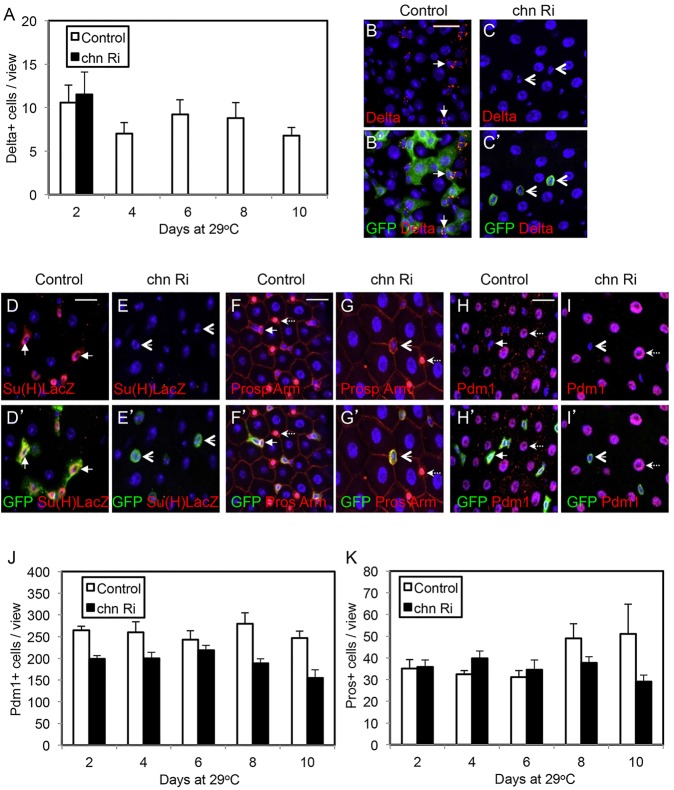
Fig. 6.
Loss of Chn does not cause precocious differentiation. The control flies were esgts>GFP crossed with w– flies, and the chn Ri were esgts>GFP crossed with UAS-chnRNAi flies. (A) The hatched flies were transferred to 29°C for the days as indicated and guts were dissected and stained for Delta. The number of Delta+ cells is significantly reduced after induction of chn RNAi (black bars) compared with control midguts (white bars). No Delta+ cells in chn RNAi samples were detected after day 4. Data are mean±s.e.m. The samples in B-C′ are from flies incubated at 29°C for 6 days. The arrows indicate examples of Delta+ staining and arrowheads indicate GFP+ cells with no Delta staining after chn RNAi. (D-E′) Similar experiments after an 8-day incubation at 29°C. The size of the GFP+ cells in RNAi midguts remained small but no expression of the EB reporter Su(H)LacZ was detected (arrowheads). (F-G′) The esg>GFP+ cells (arrows) and the nuclear Prospero staining (dashed arrows) normally do not overlap in control guts. After chn RNAi, the GFP+ cells were still separate from Prospero+ cells (arrows versus dashed arrows). (H-I′) Similarly, the esg>GFP+ cell nests (arrows) did not express Pdm1, which was detectable in differentiated ECs (dashed arrows). After chn RNAi, the GFP+ cells still did not express Pdm1 (arrowheads). (J,K) Quantification of differentiated cells in control and chn RNAi guts. Images under a 40× objective were taken from the posterior midguts of control and RNAi flies. Graph shows the average numbers of Pdm1+ ECs and Prospero+ EEs at different time points after incubation of the flies at 29°C. Data are mean±s.e.m.