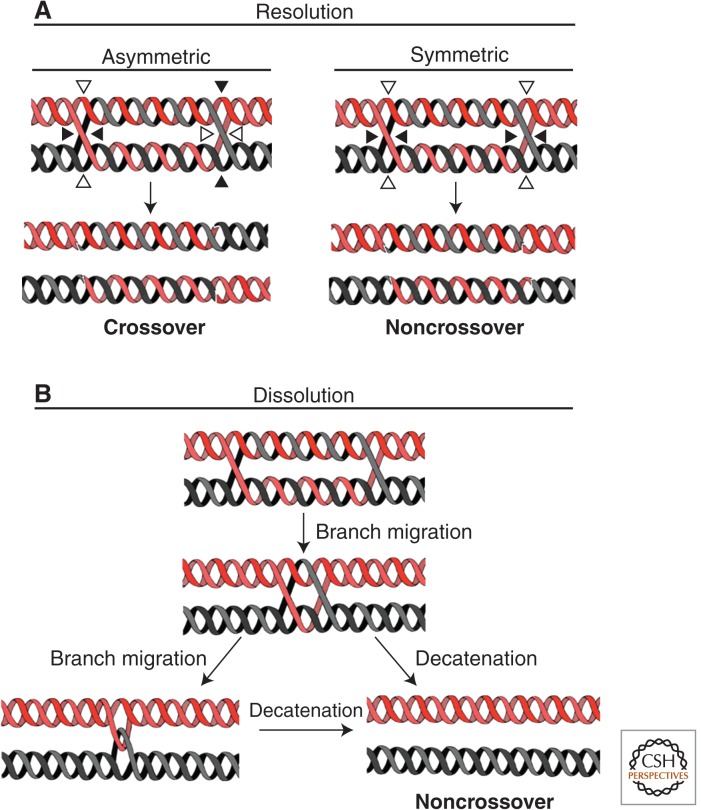
Figure 1.
Double Holliday junction processing pathways. (A) During HJ resolution, each HJ of a dHJ is cleaved by a structure-selective endonuclease (resolvase). Depending on the combination of cleavage orientations, which can be asymmetric or symmetric, this process can generate both crossover and noncrossover products. In contrast, during dissolution (B), each strand engaged in the dHJ is reassociated with its original complementary strand, preventing exchange of genetic material between the two homologous sequences (and hence generating exclusively noncrossover products). DHJ dissolution (B) is initiated by migration of the HJs toward one another. The fusion/collapse of the two HJs results in a hemicatenated intermediate. Decatenation of this intermediate regenerates the original DNA species present before the initiation of HR.