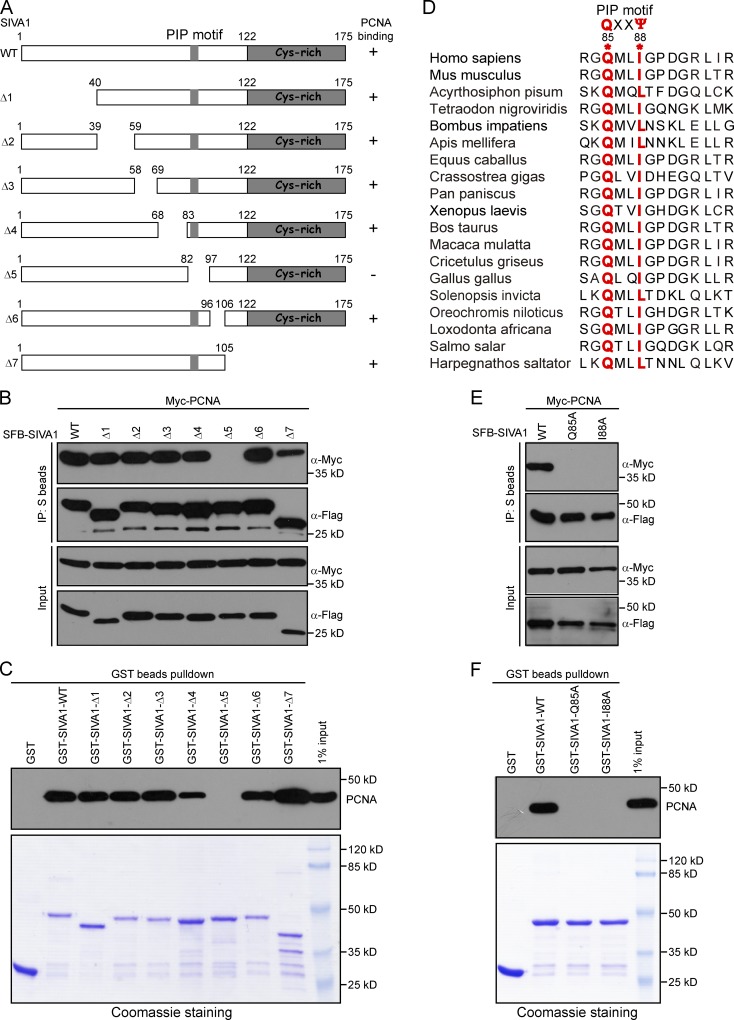
Figure 3.
The PIP box of SIVA1 is responsible for PCNA binding. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type and deletion mutants of SIVA1 used in this study. (B) Residues 83–96 of SIVA1 are responsible for PCNA binding. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding tagged PCNA and SIVA1. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with S beads, and Western blot analysis was performed with anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies. (C) Purified GST, GST-tagged wild-type SIVA1, or its deletion mutants immobilized on Sepharose beads were incubated with HEK293T cell lysates. Endogenous bound PCNA was analyzed by anti-PCNA immunoblotting. Input GST or GST-SIVA1 proteins were shown at the bottom. (D) Sequence alignment of the PCNA-binding region in SIVA1 from different species. (E and F) The PIP box of SIVA1 is required for SIVA1 to bind to PCNA. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding SFB-tagged wild-type SIVA1 or two PIP box mutants (Q85A and I88A) together with plasmids encoding Myc-tagged PCNA. (E) Coprecipitation was performed using S protein beads, and immunoblotting was performed using antibodies as indicated. (F) Purified GST or GST-tagged wild-type SIVA1 or two PIP box mutants (Q85A and I88A) immobilized on Sepharose beads were incubated with HEK293T cell lysates. Endogenous bound PCNA was analyzed by anti-PCNA immunoblotting. IP, immunoprecipitation; WT, wild type.