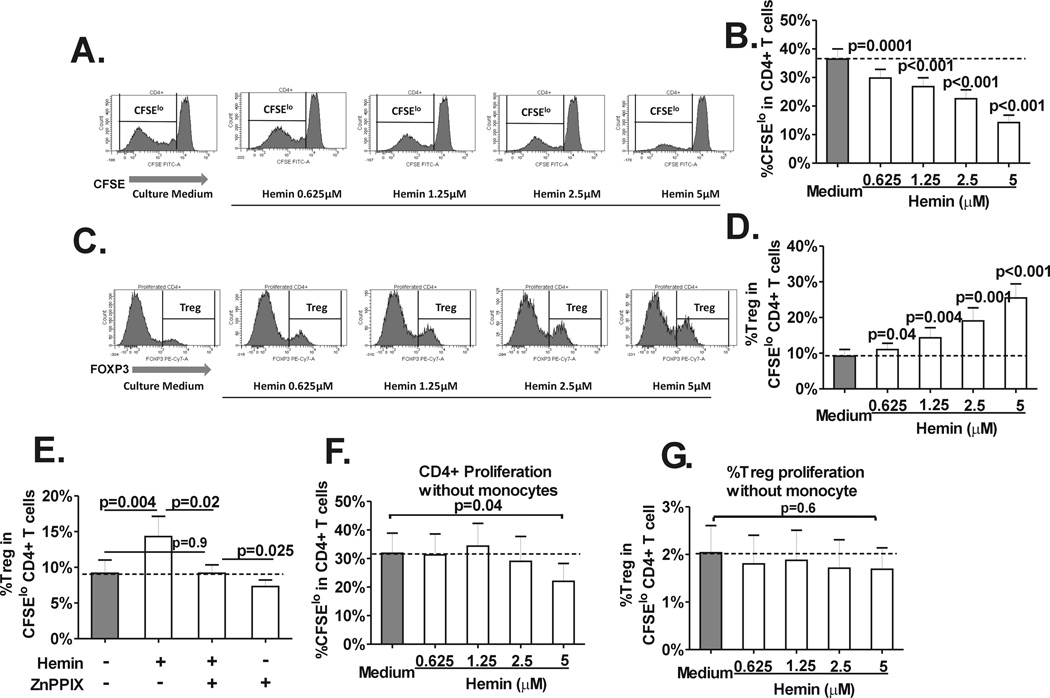
Fig. 1. Hemin induces CD4+ Treg polarization.
Purified, CFSE-stained CD4+ T cells from normal healthy volunteers (n=14) were co-cultured with autologous purified total monocyte fraction in the absence (“Culture medium”) or presence of various concentrations of hemin (0 to 5µM) and stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody for 7 days. (A) Representative histograms of the staining pattern of CFSE in total CD4+ T cells after 7 days in cocultures showing the gating used to measure the extent of CD4+ T cell proliferation defined as the frequency of divided (CFSElo) population. (B) Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of hemin on the frequency of CD4+ T cell proliferation (CD4+CFSElo cells) in T cell-monocyte cocultures from healthy controls. P values were analyzed by paired t test comparing before (“medium”) and after addition of hemin. (C) Representative histograms of the staining pattern of T cell subset expressing Foxp3hi (Tregs) within the CD4+CFSElo population in cocultures untreated or treated with various concentrations of hemin (0 to 5µM) showing the gating used to analyze the frequency of Treg population that had undergone proliferation. (D) Dose dependent increase in the frequency of Tregs in divided CD4+ T cells in the same (C) cocultures. (E) Frequency of divided Tregs in cocultures without or with addition of hemin (1.25µM) and/or HO-1 inhibitor ZnPPIX (2.5 µM) at day 0. The dotted line marks the basal Treg proliferation (minus hemin or ZnPPIX). Frequency of (F) total CD4+ and (G) Treg proliferation in cocultures treated with different doses of hemin in the absence of monocytes are shown. Unlike cocultures with monocytes, Treg proliferation is not affected by hemin and total CD4+ proliferation is only inhibited at the highest hemin concentration (5 µM). All statistical analysis indicated by p values was performed by paired t test.