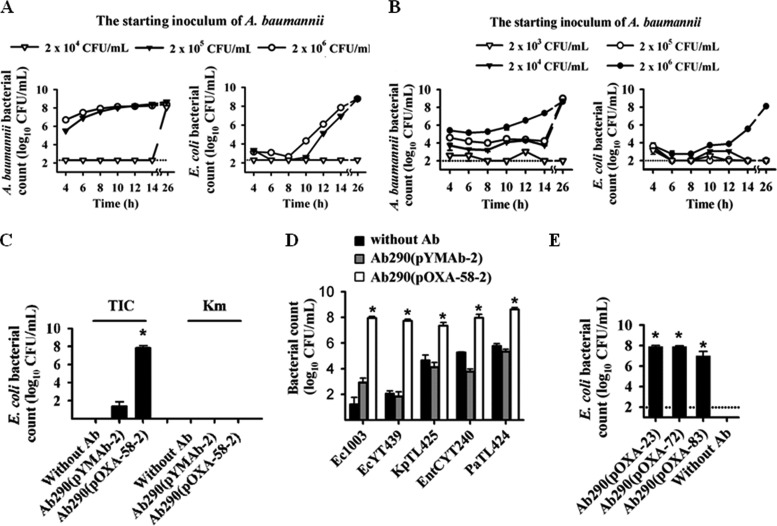
FIG 1.
Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamases (CHDLs) confer shelter to carbapenem-susceptible bacteria. (A and B) A carbapenem-susceptible Escherichia coli strain (Ec1003) (104 CFU/ml) was cocultured with different amounts of a clinical A. baumannii isolate producing OXA-58 (Ab1969) (A) or an A. baumannii transformant producing OXA-58 [termed Ab290(pOXA-58-2)] (B) in the presence of imipenem. In panel B, although A. baumannii Ab290(pOXA-58-2) could survive under the culture condition at an inoculum of 104 CFU/ml or higher (left panel), E. coli Ec1003 was protected from carbapenem killing only at 106 CFU/ml of Ab290(pOXA-58-2) (right panel). (C) At 106 CFU/ml, Ab290(pOXA-58-2) sheltered Ec1003 against ticarcillin (TIC) but not kanamycin (Km) killing. The control Ab290(pYMAb-2) transformant, which carries an empty shuttle vector, failed to exert the sheltering effect. The experiment was also performed without A. baumannii (Without Ab). (D) Sheltering effect of A. baumannii Ab290(pOXA-58-2) for other Gram-negative bacteria against carbapenem-induced death. The first two or four letters of the strain designations indicate the species as follows: Ec, E. coli; Kp, Klebsiella pneumoniae; EntC, Enterobacter cloacae; Pa, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. (E) Ab290 transformants producing other CHDL proteins, including OXA-23, -72, and -83, sheltered Ec1003 against carbapenem-induced death. Each symbol in panels A and B is the mean of triplicate results. The dotted lines in panels A, B, and E indicate the detection limit. The bars and error bars in panels C to E indicate the means and standard deviations, respectively, of triplicate tests. Values that are significantly different (P < 0.05) are indicated by an asterisk.