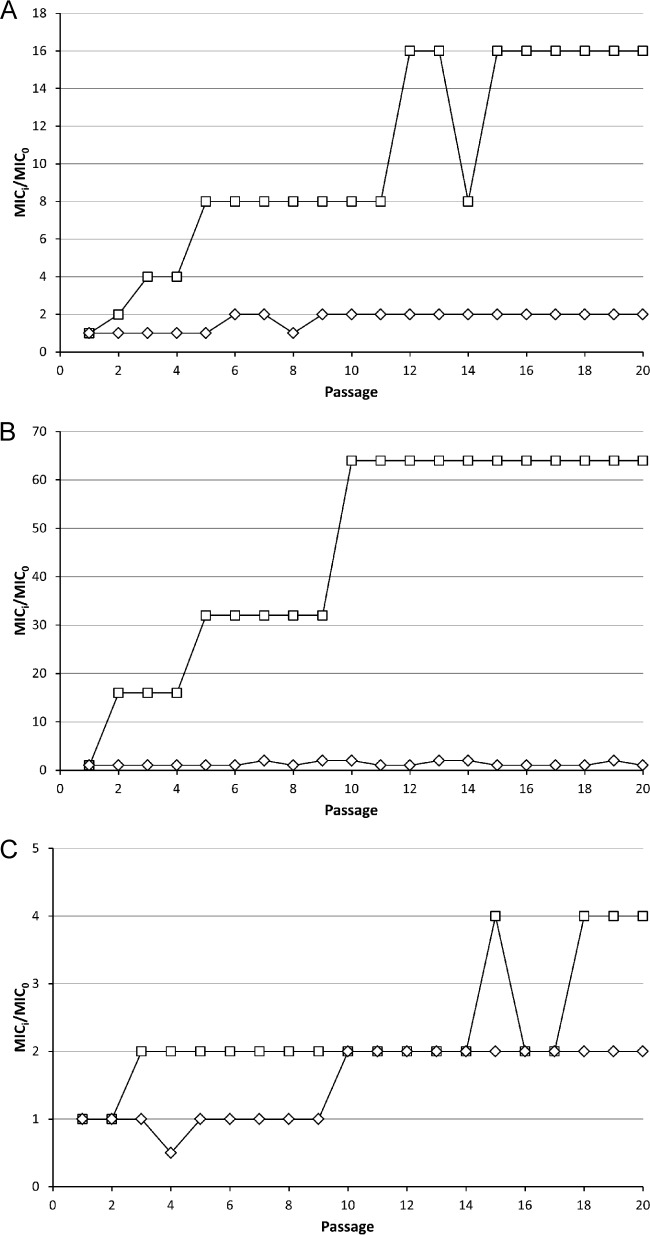
FIG 3.
Resistance development against Art-175 and ciprofloxacin. A laboratory strain of clinical origin (P. aeruginosa PAO1) (A), an environmental strain (P. aeruginosa Br257) (B), and a multidrug-resistant strain (P. aeruginosa Br776) (C) were serially exposed to subinhibitory concentrations to select for decreased susceptibility. Over 20 passages, the MIC of Art-175 (◊) increased 2-fold, whereas the MIC of ciprofloxacin (☐) increased 16- (PAO1), 64- (Br257), or 4-fold (Br776).