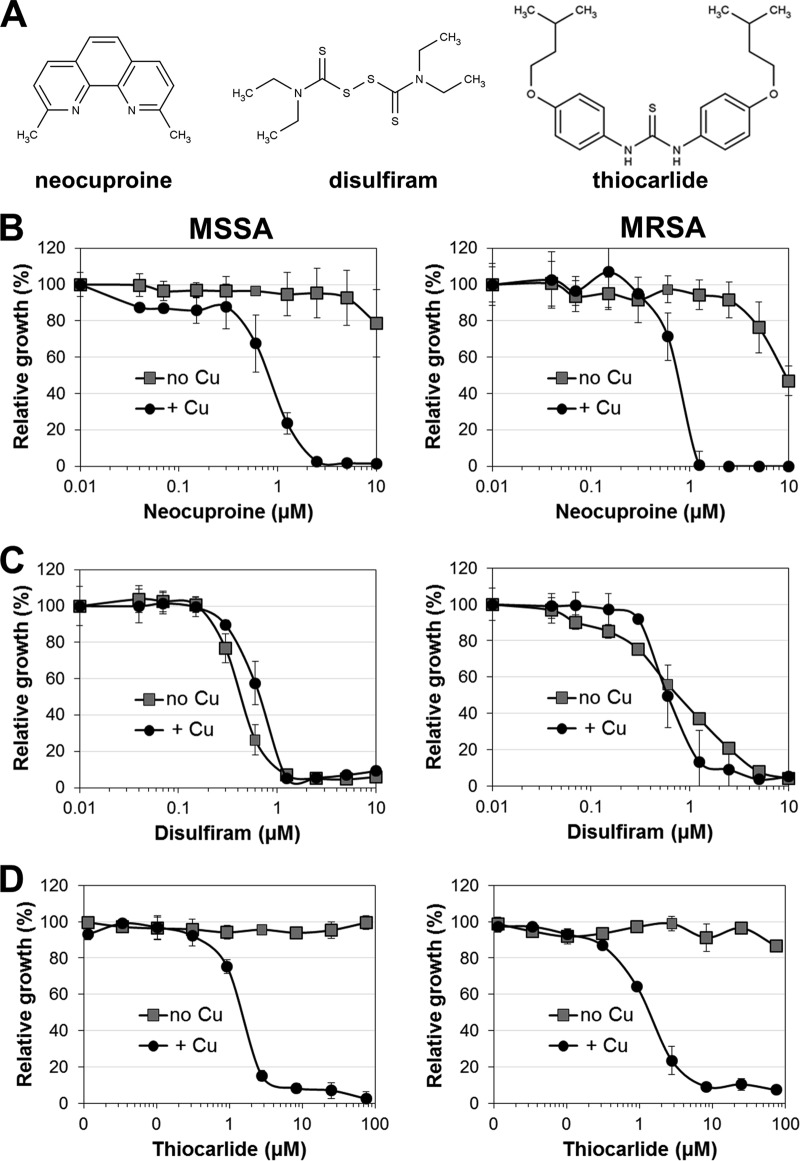
FIG 1.
Identification of copper-dependent anti-MRSA compounds. The random compound library used for a proof-of-concept screen was spiked with several compounds with reported potential copper-complexing ability, some of which were found to be antibacterial compounds. (A) Molecular structures of neocuproine, disulfiram, and thiocarlide. (B to D) The antibacterial activities of neocuproine (B), disulfiram (C), and thiocarlide (D) were plotted over the respective drug concentration for trace copper (no Cu) and copper-supplemented (+ Cu) conditions. (Left) Experiments performed using a clinical MSSA strain; (right) data obtained using a clinical MRSA strain. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and the means ± standard deviations are presented for each drug concentration. Data are representative of those from at least three independent experiments.