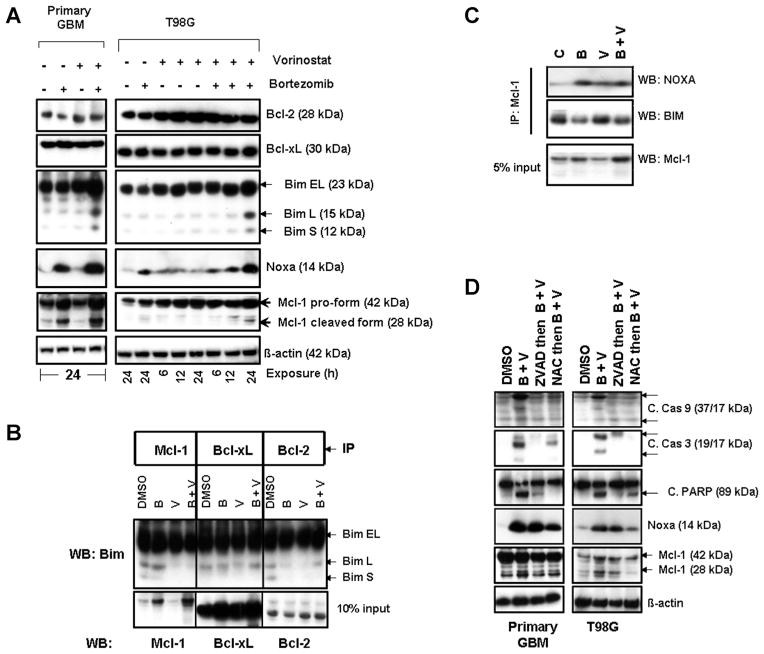
Figure 4.
Co-treatment with bortezomib and vorinostat induces Noxa, disrupts Mcl1/Bim complexes, and activates Bak and Bax. (A) Primary tumor and T98G cells were treated with bortezomib (5 nM) or vorinostat (2 μM) or the combination for the durations noted. Cell extracts were prepared, and equal amounts of protein were separated by SDS–PAGE and subjected to Western blotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. β-actin served as loading control. (B) T98G cells were treated with inhibitors for 24 h. An equal amount of protein was immunoprecipitated (IP) with the indicated antibodies as described in the Materials and Methods Section. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis using anti-Bim antibody. Samples of whole cell lysates (WCL) were subjected to Western blot analysis to monitor the total levels of the respective proteins. (C) T98G cells were treated with inhibitors for 24 h as described in “A.” To assess the association of Mcl-1 and Noxa or Bim, immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using Mcl-1 antibody. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis. Samples of whole cell lysates (WCL) were subjected to Western blot analysis to monitor the total levels of Mcl-1. (D) Primary tumor and T98G cells were pretreated with 25 μM ZVAD-fmk (pan caspase inhibitor) or 5 mM NAC (ROS scavenger) for 2 h followed by the combination of bortezomib (5 nM) plus vorinostat (2 μM, B + V) for 24 h. Control cells received an equivalent amount of DMSO. Western blot analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies. β-actin served as loading control.