Fig. 3.
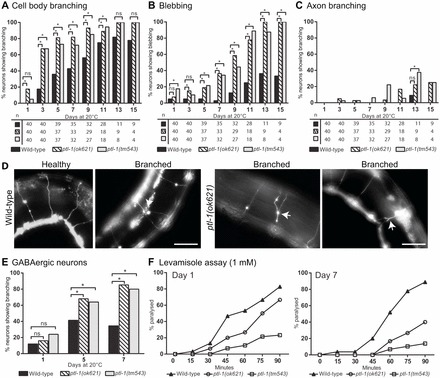
ptl-1(ok621) and ptl-1(tm543) mutant strains show defects in maintaining neuronal integrity with age in touch receptor and GABAergic neurons. Neurons were visualised using the Pmec-4::gfp reporter for touch receptor neurons or the Punc-47::gfp reporter for GABAergic neurons. Worms were imaged every second day from day 1 to day 15. For imaging assays, the χ2 test for independence was used to analyse differences between genotypes. (A–C) Anterior touch neurons in ptl-1 mutants scored for (A) cell body branching, (B) blebbing along the axon and (C) axon branching. Sample sizes are indicated below graphs. (D) Representative image of the phenotype scored in GABAergic neurons, showing healthy neurons and a branched commissure in wild-type, and representative images of branched commissures in ptl-1(ok621) worms. Arrows indicate branching. Scale bars: 50 µm. (E) Data for the incidence of branching in GABAergic neurons for ptl-1 mutant strains. (F) Assay for paralysis after levamisole exposure. Worms were scored for paralysis over 90 minutes on drug plates on day 1 and day 7 of adulthood (n = 30). Statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA; ptl-1(ok621) and ptl-1(tm543) mutant strains, but not wild-type controls, show significant decreases in drug sensitivity between day 1 and day 7. ns, no significance; *P<0.05.
