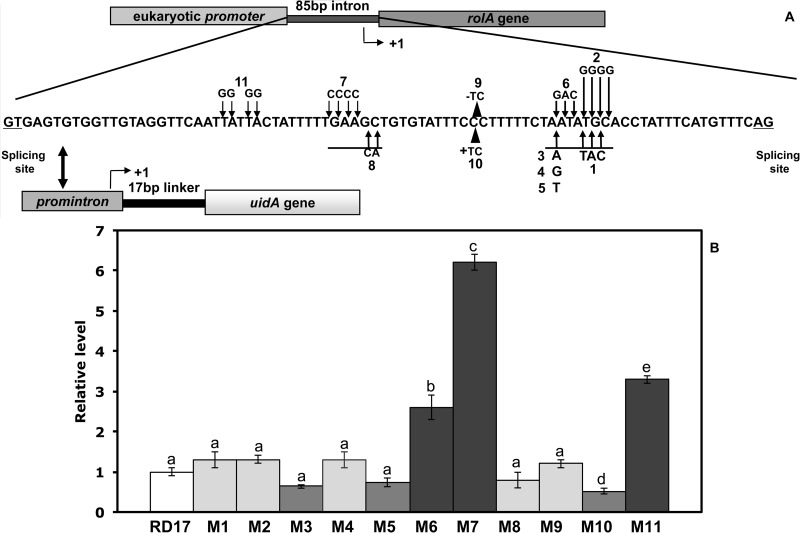
FIG 1.
(A) Schematic drawing of the chimeric reporter gene. The position of the major transcriptional start site (+1) is identified by an arrowhead, and the −10 and −35 sequences are underlined. The different mutations are also indicated. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the uidA gene in S. meliloti cells containing the wild type (RD17) and the mutated 85-17-uidA construct. Values are the averages ± standard deviations of the results from four biological replicates conducted at different times. Relative gene expression levels determined by the comparative CT method are presented as follows: 2−ΔΔCT > 1, more highly expressed genes in cells transformed with the mutated construct (RD65, RD66, and RD67 cells); 2−ΔΔCT < 1, more highly expressed genes in cells transformed with the wild-type construct (RD64 cells). Different letters are used to indicate means that differ significantly according to Tukey's test (P < 0.05). The numbers refer to the mutations described in Table 1.