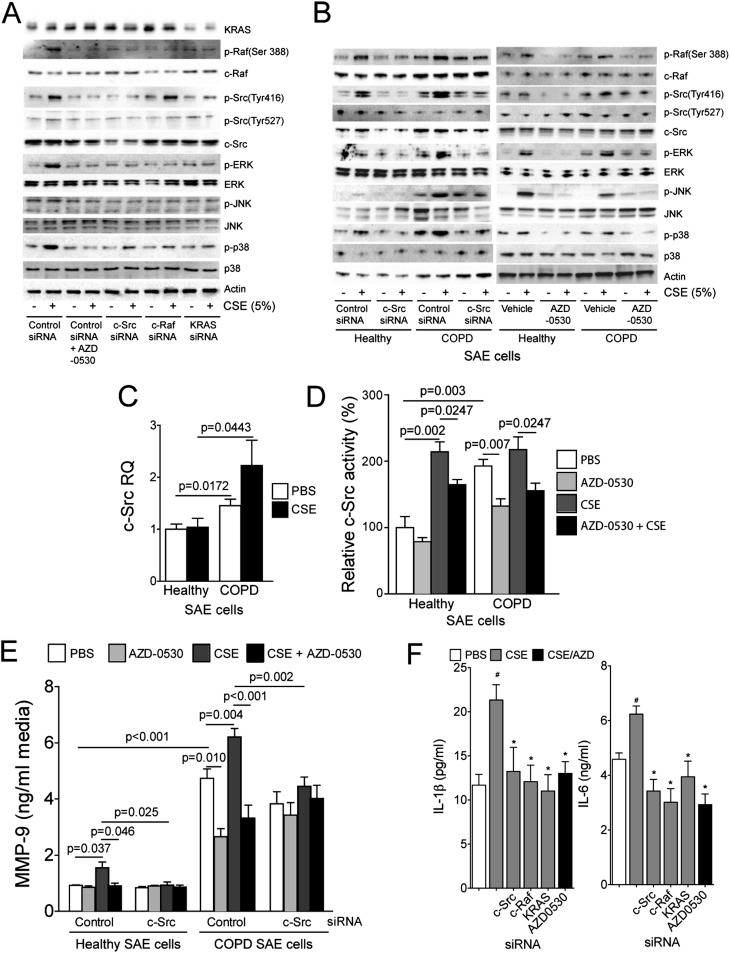
Figure 2.
Chemical and gene-specific inhibition of c-Src prevents smoke-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation in a KRAS/c-Raf1–dependent manner. (A) Small airway epithelial (SAE) cells were examined for c-Src, c-Raf, and MAPK phosphorylation after transfection with negative control, c-Src, c-Raf, or KRAS small interfering RNA (siRNA) and treatment with cigarette smoke extract (CSE) (90 min) and AZD-0530. (B) Immunoblots were performed to determine phosphorylation and total protein levels of c-Src, c-Raf, and the MAPK proteins in SAE cells from healthy subjects and from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who underwent Src inhibition by siRNA or AZD-0530. (C–E) c-Src gene expression compared with GAPDH (C), c-Src activity (D), and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 levels (E) in media were examined. Graphs are represented as mean ± SEM of 12 measurements. P values are shown comparing both treatments connected by a line. (F) IL-1β and IL-6 levels in media were examined in cells after transfection with negative control, c-Src, c-Raf, or KRAS siRNA and treatment with CSE (90 min) and AZD-0530. #Significant change compared with PBS-treated cells. *Significant change compared with control siRNA cells treated with CSE.