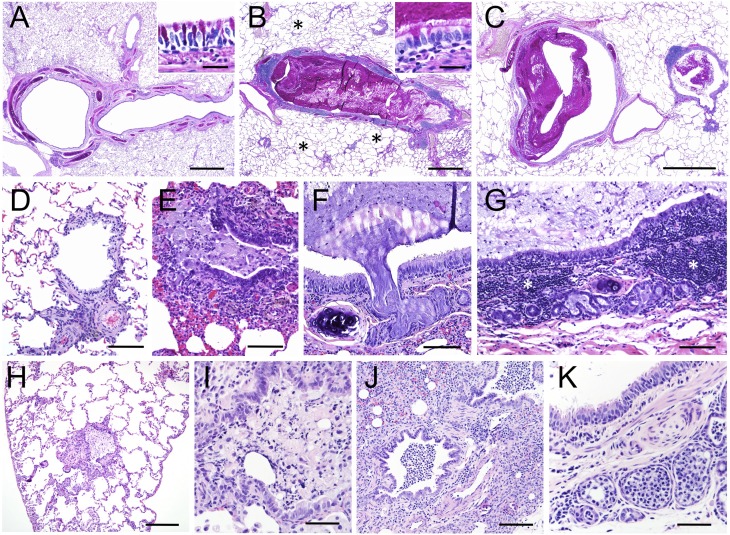
Figure 4.
Histopathology in the CF ferret lung. Lungs from four CF animals ranging from 3–8 months of age are shown. (A–C) Proximal airway mucus obstruction in a CF animal demonstrating complete occlusion (B) and partial occlusion (C) as compared with the non-CF control (A). Insets in (A) and (B) are higher-power images of the surface airway epithelium. (D and E) Distal airway occlusion in a CF (E) as compared with non-CF (D) animal. (F–G) Submucosal gland plugging with mucus (F and G) and expansion of bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue (G) in a proximal airway of a CF animal. (H and I) Distal airway occlusion in two different CF animals with inflammatory cell debris in the lumen. (J and K) Accumulation of inflammatory cells in the lumen of a distal airway (J) and submucosal glands (K) extending into alveoli from a CF animal. The four independent CF animals are grouped in panels as follows: (B, C, and E–G), (H), (I), (J and K). Images in (A–C) are periodic acid-Schiff stains and (D–K) are hematoxylin and eosin stains. Scale bars, 1 mm (A–C), 200 μm (H), 100 μm (D–G, J), 50 μm (I and K). *Air-trapping in CF lung (B).