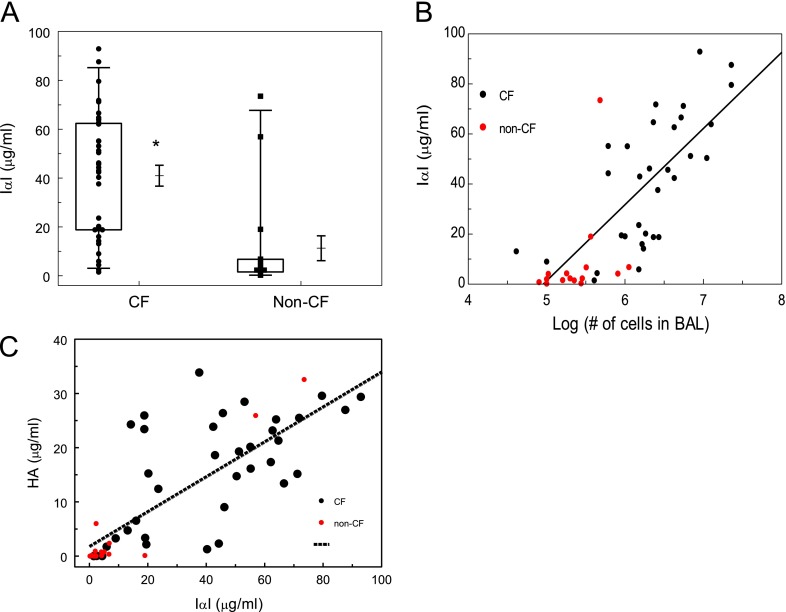
Figure 1.
Children with cystic fibrosis (CF) have increased concentrations of inter-α-inhibitor (IαI) in their bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (A) Samples were stratified according to the primary diagnosis (CF = cystic fibrosis; Non-CF = lower airway disease). IαI was measured in the cell-free lavage as described in Materials and Methods. Box whisker plots showing individual data points, boxes, whiskers (2 SD from the mean), means, and standard errors (*P = 0.0.0026 with Mann-Whitney test; n = 16 for Non-CF and n = 36 for CF). (B) IαI concentrations versus log10 (number of inflammatory cells) in the BALF for patients with CF and non-CF subjects. The straight line represents best line of fit for the CF samples (IαI = 30.43 × log (cells) of cells −150; R = 0.7; P < 0.001). (C) Hyaluronan (HA) versus IαI in the BALF. The straight line represents best line of fit for all patients (R2 = 0.6; P < 0.05).