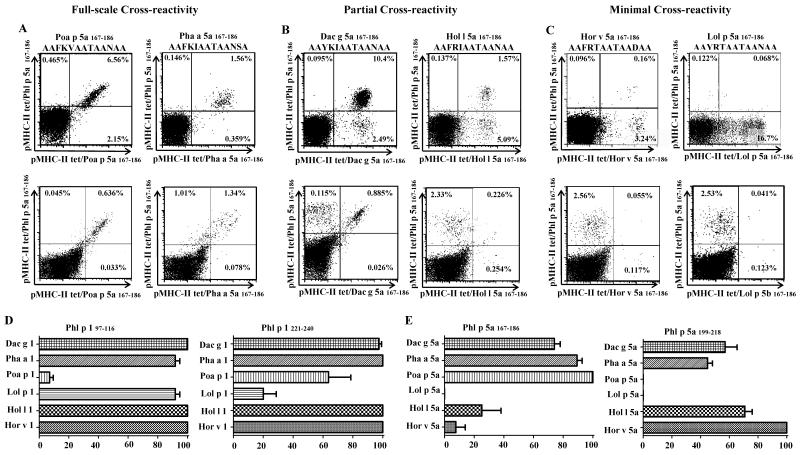
Figure 2.
Grass-specific CD4+ T-cells exhibit varying degrees of cross-reactivity. After in vitro stimulation with Phl p homologous grass peptides (top panels of A, B and C, amino-acid sequence of the stimulating peptide is specified on top of each panel) or Phl p 167-186 AAFKVAATAANAA, bottom panels of A, B and C), cells were co-stained with APC-labeled DR04:01/Phl p grass peptide-loaded tetramers (Y axis) and with PE-labeled DR04:01/homologous grass peptide-loaded tetramers corresponding to the stimulating epitopes (X axis). The plots in A, B and C show representative results for different cross-reactivity profiles for the TGP-derived epitopes in the Group 5a 167-186 region. A. Full-scale cross-reactivity was observed for Poa p 5a 167-186, and Pha a 5a 167-186. B. Partial cross-reactivity was observed for Dac g 5a 167-186 and Hol 5a 167-186. C. Minimal cross-reactivity was observed for Lol p 5a 167-186 and Hor v 5a 167-186. D. Comparison of percentages of cross-reactive T-cells for Group 1 homologs. E. Comparison of percentages of cross-reactive T-cells for Group 5a homologs. Summarized results from (n=6) allergic subjects are presented for distinct antigenic epitope regions. Each bar depicts the average of dual-tetramer stained T-cells (cross-reactive) observed per epitope.