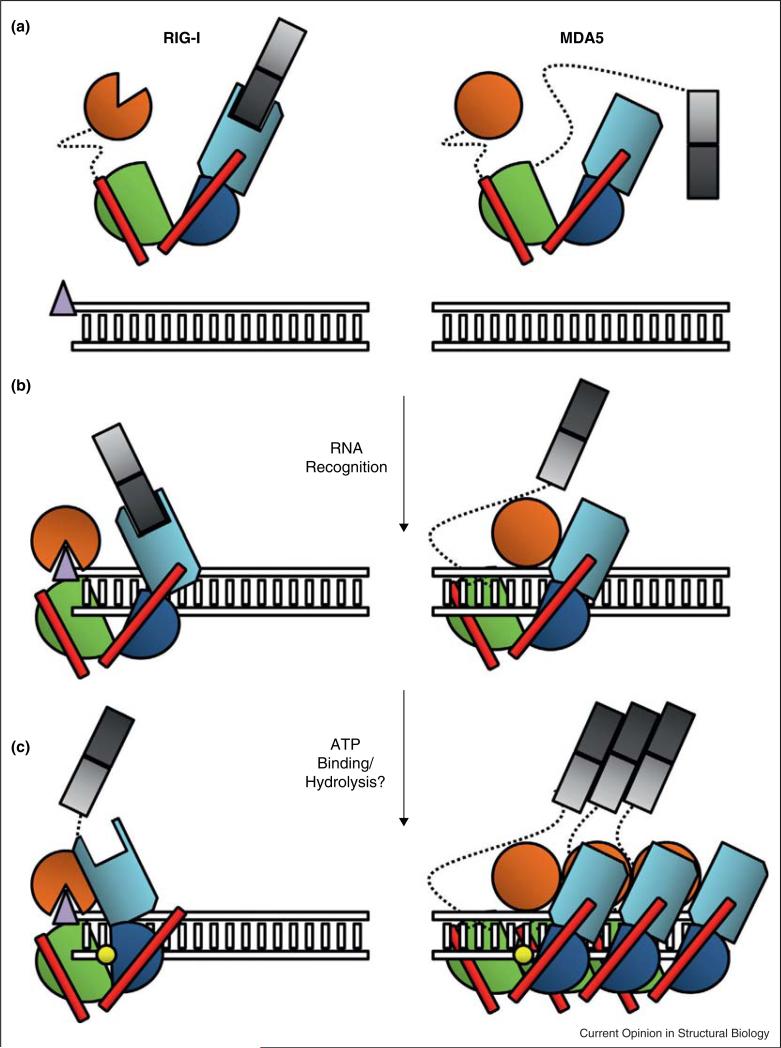
Figure 4.
Schematic representing the stages of RLR activation. RLR proteins RIG-I and MDA5 are shown color coded by domain; CARD1: light gray, CARD2: dark gray, HEL1: Green, HEL2: blue, HEL2i: Cyan, Pincer: Red, and CTD: orange. Duplex RNA is represented as a ladder, with the triphosphate moiety depicted as a purple triangle at the terminus. ATP is depicted as a yellow circle. Dotted lines represent flexible linker regions between domains. (a) RIG-I surveys the cell in a tightly regulated ‘signal off’ conformation, with the CARD domains packed tightly against HEL2i, and the CTD sampling greater conformational space. MDA5 regulation may be more attributable to its requirement for oligomerization than CARD sequestration, although the details of this hypothesis remain unclear. (b) The RIG-I CTD has an exceptionally high affinity for terminal triphosphates, thus the protein binds most strongly to the dsRNA end. The CTD caps the terminus as it interacts with the triphosphate, while the HEL1, HEL2 and HEL2i domains wrap around the duplex forming a ring. In this state, the CARDs of RIG-I can theoretically still be accommodated in a HEL2i-sequestered state. The MDA5 CTD recognizes and binds internal RNA duplexes, in conjunction with the HEL1, Hel2 and HEL2i domains. Notably, the CTD resides closer to the HEL2i domain in MDA5 than in RIG-I, resulting in a more C-shaped than O-shaped conformation. (c) Upon interaction with ATP, the RIG-I helicase domain further compacts, potentially ejecting the CARDs, which become available for interaction with other protein factors and subsequent signaling through MAVS. MDA5 forms a cooperative filament along the RNA substrate, bringing the CARD domains in sufficient proximity to multimerize and promote signaling. The role of ATP in this process remains unclear. CARD: Caspase Activation and Recruitment Domain, CTD: C-terminal Domain.