Table I.
Glossary for Parameters and Variables
| Parameter/variable (unit) | Definition | References/remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Full PBPK model | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| K 0 (M/h) | Endogenous IgG production rate | (13) |
| Q organ (L/h) | Plasma Flow rate to each organ | (10) |
| L organ (L/h) | Lymphatic Flow rate to each organ | (10) |
| CLOrganUptake (L/h) | Endosomal uptake rate of unbound antibody | (13) |
| CLOrganProteolysis (L/h) | Clearance rate of unbound antibody via proteolytic degradation in the endosome | Same value for CL OrganUptake. |
| k on-X (M−1 h−1) | mAb-FcRn association constant in each subendosomal compartment X | (13) Assumed similar for IgG and mAb |
| k off-X (h−1) | mAb-FcRn dissociation constant in each subendosomal compartment X | (13) Assumed similar for IgG and mAb |
| KA (M)−1 | Equilibrium binding association affinity |
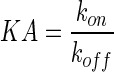
|
| RtotalOrgan ‐ X (moles) | Initial amount of free FcRn receptor in subendosomal compartment X | obtained by multiplying FcRn concentration reported in (13) by V OrganEND |
| F return (no units) | Fraction of antibody returning from lymph node to plasma |
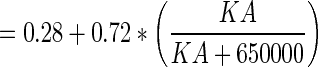 (13) (13) |
| τ (h) | Transit time between endosomal compartments | (13) (0.045) |
| TauLN (h) | Transit time from lymph node to plasma | (13) (9.1) |
| σ VAS (no unit) | Vascular reflection coefficient | Same for all organs (0.95) (11) |
| σ LY (no unit) | Lymph reflection coefficient | Same for all organs (0.2) |
| FR (no unit) | Recycling fraction of the bound antibody from endosomal to vascular and interstitial subcompartments | (11) (0.715) |
| V OrganVAS (L) | Volume of vascular compartment in each organ | (11) |
| V OrganISF (L) | Volume of interstitial compartment in each organ | (11) |
| V OrganEND (L) | Volume of each endosomal subcompartment in each organ | (11) |
| V Plasma (L) | Volume of plasma | (11) |
| - Variables | ||
| A JPlasma (moles) | Amount of endogenous IgG or mAb in plasma | |
| A JLN (moles) | Amount of endogenous IgG or mAb in lymph node | |
| A JVAS Organ (moles) | Amount of endogenous IgG or mAb in vascular space | |
| A JISF Organ (moles) | Amount of endogenous IgG or mAb in interstitial space | |
| A JEND Organ ‐ X (moles) | Amount of endogenous IgG or mAb in subendosomal compartment X | |
| ARCPXJOrgan ‐ X (moles) | Amount of endogenous IgG -FcRn or mAb-FcRn receptor complex in subendosomal compartment X | |
| Step 1 (Fig. 2) | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| k OrganVAS ‐ circul. (h−1) | Transfer rate from vascular compartment to lung or, in case of lung, from lung to plasma |
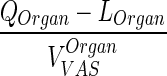
|
| k Organcircul. ‐ VAS (h−1) | Transfer rate from plasma to vascular compartment |
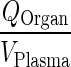
|
| (1 − σ VAS) × k OrganLY VAS ‐ ISF (h−1) | Transfer from vascular to interstitial compartment via lymphatic flow |
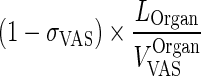
|
| k OrganVAS ‐ EL (h−1) | Elimination from vascular compartment |

|
| k OrganVAS ‐ VAS (h−1) | Input from vascular compartment to itself. Reflect endosomal contribution to vascular compartment |
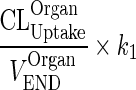
|
| k OrganVAS ‐ ISF (h−1) | Transfer from vascular to interstitial compartment |
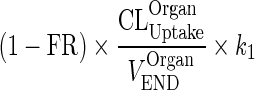
|
| k OrganISF ‐ VAS (h−1) | Transfer from interstitial to vascular compartment |
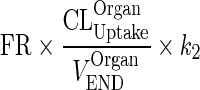
|
| (1 − σ LY) × k OrganLY ISF ‐ LN (h−1) | Transfer from interstitial compartment to lymph node via lymphatic flow |
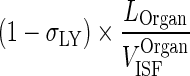
|
| k OrganISF ‐ EL (h−1) | Elimination from interstitial compartment |
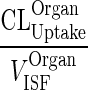
|
| k OrganISF ‐ ISF (h−1) | Input from interstitial compartment to itself. Reflect endosomal contribution to interstitial compartment |
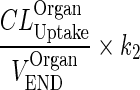
|
| KDEND (moles) | Equilibrium dissociation constant for mAb binding to FcRn receptor in amounts |
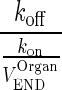
|
| K 0 (M/h) | Endogenous IgG production rate | (13) |
| - Variables | ||
| A JEND Total Organ ‐ X (moles) | Total amount of endogenous IgG or mAb (bound and free) in subendosomal compartment X | |
| Steps 2 and 3 (Fig. 3a and b) | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| Q Visceral (L/h) | plasma Flow rate to the visceral compartment | Q Heart + Q Kidney + Q Skin + Q Muscle |
| Q Splanchnic (L/h) | plasma Flow rate to the splanchnic compartment | Q GIT + Q Spleen |
| L Visceral (L/h) | Lymph Flow rate to the visceral compartment | L Heart + L Kidney + L Skin + L Muscle |
| L Splanchnic (L/h) | Lymph Flow rate to the splanchnic compartment | L GIT + L Spleen |
| - New compartments resulting from model simplification | ||
| Splanchnic | GIT and spleen | |
| Visceral | Heart, kidney, skin, and muscle lumped | |
| Steps 4, and 5 (Fig. 3c and d) | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| Q Peripheral (L/h) | Plasma Flow rate to the Peripheral compartment | Q Visceral + Q Splanchnic |
| L Peripheral (L/h) | Lymph Flow rate to the Peripheral compartment | L Visceral + L Splanchnic |
| - New compartments resulting from lumping | ||
| Peripheral | Visceral and splanchnic | |
| Step 6 (Fig. 3e) | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| k CentralEL (h−1) | Elimination rate from the central compartment | |
| (1 − σ VAS) × k CentralLY Central ‐ Per (h−1) | Transfer rate from the central to interstitial (i.e., peripheral) compartment via lymphatic flow | |
| k CentralCentral (h−1) | First-order input from central compartment to itself which reflects the impact of recycled drug from endosomal compartment | |
| k CentralCentral ‐ ISF (h−1) | First-order input from central to interstitial (i.e., peripheral) compartment | |
| k PeripheralISF ‐ Central (h−1) | Transfer from interstitial (i.e., peripheral) to central compartments | |
| (1 − σ LY) × k PeripheralLY ISF ‐ LN (h−1) | Transfer from interstitial (i.e., peripheral) compartment to lymph node via lymphatic flow | |
| k PeripheralISF ‐ ISF (h−1) | Input from Peripheral compartment to itself. Reflect endosomal contribution to interstitial compartment | |
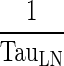 (h−1) (h−1) |
Transfer from lymph node to Central compartment | |
| Variables | ||
| A Central (moles) | Amount of mAb in the central compartment (i.e., plasma and Vascular subcompartments in equilibrium) | |
| A Peripheral (moles) | Amount of mAb in the Peripheral compartment | |
| Step 7 (Fig. 3f) | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| k CEL (h−1) | Elimination rate from the central compartment after subtracting the contribution of the endosomal compartment | |
| k PEL (h−1) | Elimination rate from the peripheral compartment after subtracting the contribution of the endosomal compartment | |
| k Cen ‐ Per (h−1) | Reflection of the fraction mAb-FcRn complex recycled | |
| (1 − σ VAS) × k CentralLY ‐ ISF (h−1) | Transfer of the mAb from Central to Peripheral compartments via lymphatic flow | |
| k CP (h−1) | Transfer of the mAb from Central to Peripheral compartments via two processes, a- the lymphatic flow and b- the reflection of the fraction mAb-FcRn complex recycled | (1 − σ VAS) × k CentralLY ‐ ISF + k CentralCentral ‐ ISF |
| (1 − σ LY) × k PeripheralLY ISF ‐ LN (h−1) | Transfer from interstitial (i.e., peripheral) compartment to lymph node via lymphatic flow | |
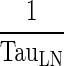 (h−1) (h−1) |
Transfer from lymph node to Central compartment | |
| Final simplified model (Fig. 4) | ||
| - Parameters | ||
| V C (L) | Volume of the Central Compartment | |
| k EL (h−1) | Elimination rate from the central and peripheral compartments | |
| k CP (h−1) | Transfer of the mAb from Central to Peripheral compartments via two processes, a- the lymphatic flow and b- the reflection of the fraction mAb-FcRn complex recycled | (1 − σ VAS) ∗ k CentralLY − ISF + k CentralCentral − ISF |
| k LN (h−1) | Transfer from interstitial (i.e., peripheral) compartment to lymph node via lymphatic flow and Transfer from lymph node to Central compartment | |
