Figure 1. Transcriptome alterations with HSC aging.
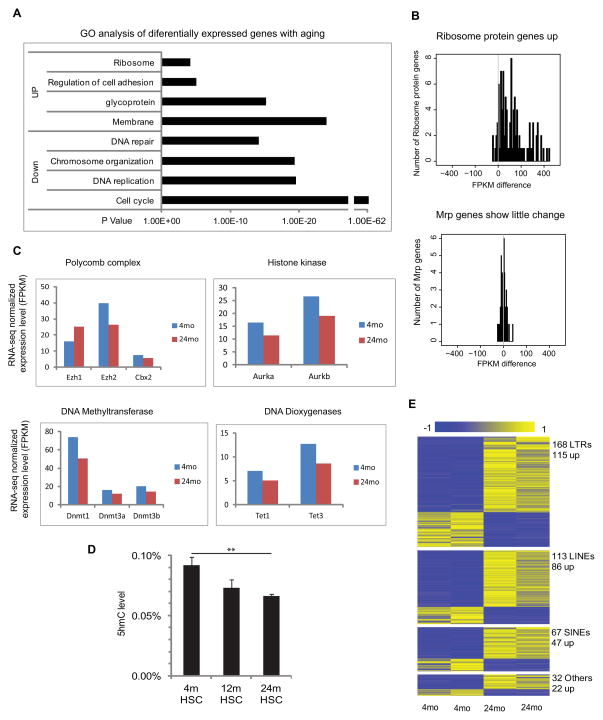
(A) Gene ontology enrichment analysis for 2140 differentially expressed genes with HSC aging; X-axis shows the P value.
(B) The distribution of expression changes for ribosomal protein genes during HSC aging, where the x-axis value is FPKM difference between Old and Young HSC.
(C) Average FPKM value of genes encoding epigenetic modifiers in young and old HSCs.
(D) HPLC-mass-spectrometry measurements of 5-hydroxy methylcytosine (5hmc) levels as a proportion of the total cytosine in purified HSCs from 4mo, 12mo and 24mo old mice (n=7). ** P< 0.01. Error bars represent Mean ± SEM.
(E) Differential expression of repetitive elements during HSC. Each row represents a repeat location in the genome. Blue denotes low and yellow high expression (log2 reads number).
See also Figures S1, and S2