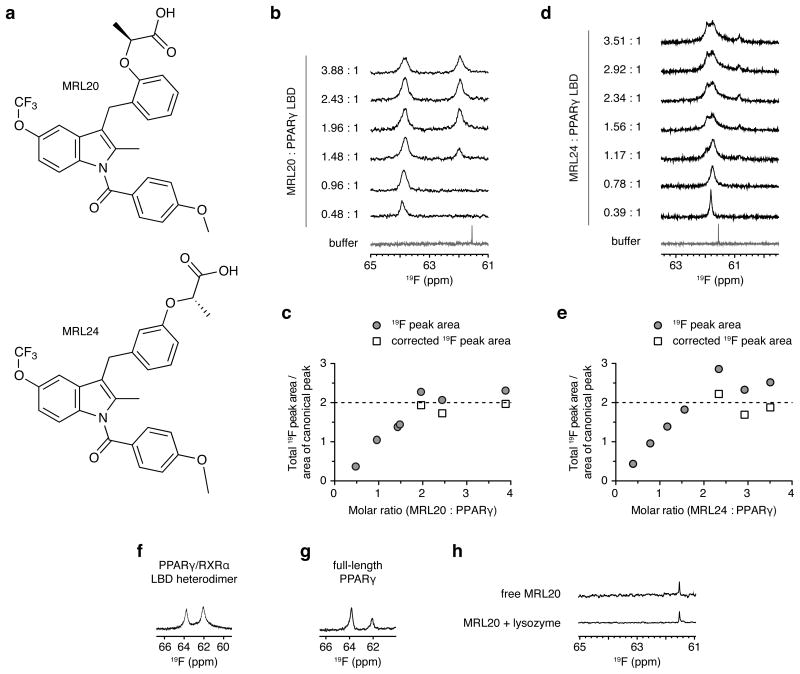
Figure 1. MRL20 and MRL24 bind to PPARγ with a 2:1 stoichiometry.
(a) Chemical structure of MRL20 and MRL24. Titration of (b,c) MRL20 or (d,e) MRL24 results in the population of two PPARγ LBD-bound 19F NMR resonances, where (c,e) are a plot of the total 19F peak area in (b) and (c), normalized to the area of the saturated canonical peak; concentrations beyond two molar equivalents of ligand are corrected (free ligand signal subtracted and adjusted for differential longitudinal relaxation; see methods for details). (f,g) MRL20 populates two 19F NMR resonances within the context of the (f) PPARγ/RXRα LBD heterodimer and (g) full-length PPARγ. (h) A single, sharp 19F resonance is observed for free MRL20 in buffer or added to lysozyme, indicating that alternate site binding of MRL20 to PPARγ occurs in a specific manner.