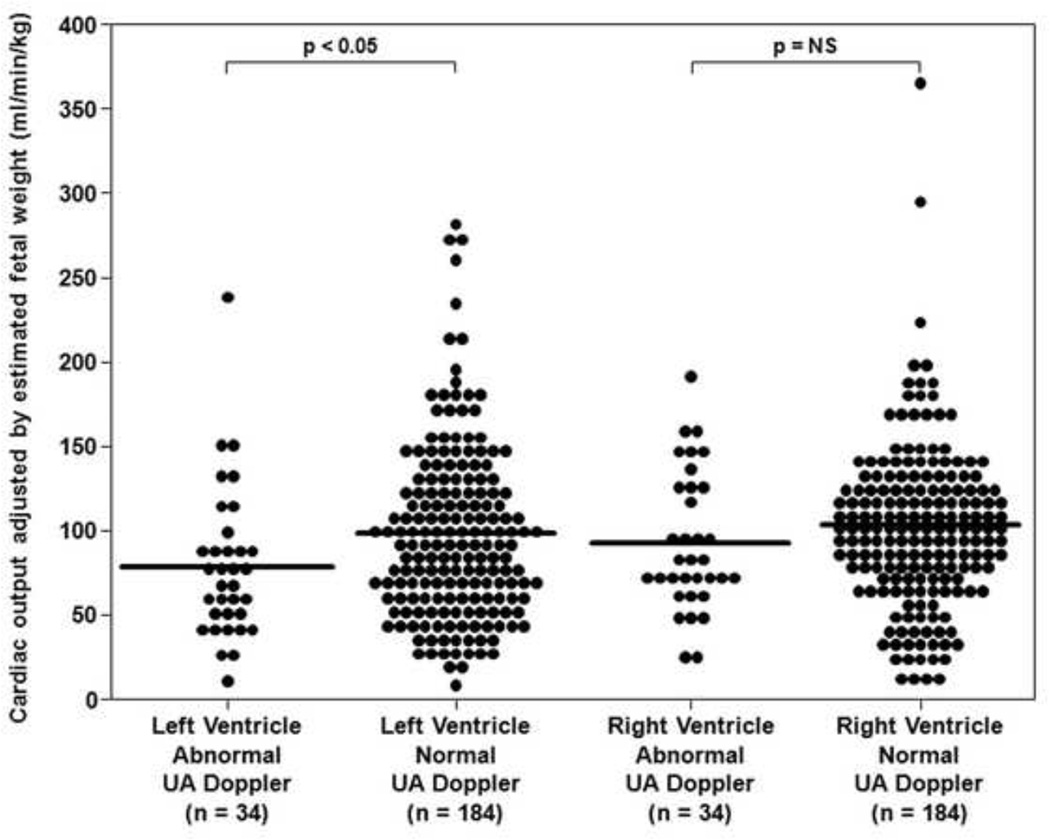
Figure 3. Cardiac output adjusted by estimated fetal weight of the left and right ventricles in the presence of increased placental vascular impedance to flow.
Cardiac output adjusted for estimated fetal weight (EFW) in fetuses with an umbilical artery (UA) pulsatility index > 95th percentile (ABN) were compared to 184 normal fetuses (NL).40 For the left ventricle, the median CO adjusted for EFW (mL/min/kg) was significantly lower in the presence of increased placental vascular impedance to flow (ABN: 67.8, IQR: 44.7 – 84.1 vs. NL: 90.0, IQR: 56.0 – 127.5; p < 0.05). However, for the right ventricle, the median CO adjusted for EFW (mL/min/kg) was not significantly different between ABN and NL groups (ABN: 77.4, IQR: 66.1 – 123.8 vs. NL: 99.9, IQR: 72.2 – 126.0; p = NS).