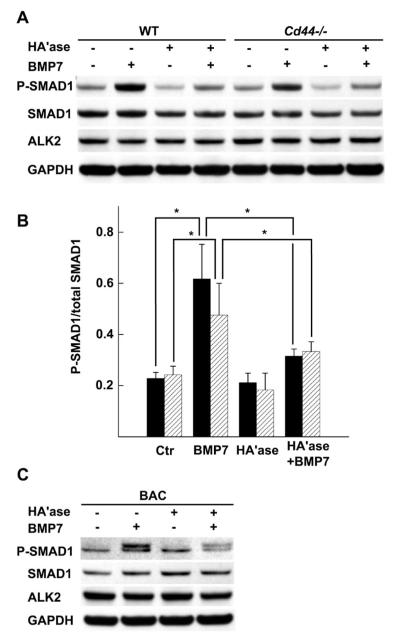
Figure 5.
Effect of hyaluronidase pretreatment on Smad1 phosphorylation in response to bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP-7) in chondrocytes from wild-type (WT) mice and CD44−/− mice. A, WT and CD44−/− murine chondrocytes were pretreated with testicular hyaluronidase (HAase), stimulated with BMP-7, and analyzed by Western blotting for Smad1 phosphorylation (p-Smad1), total Smad, and activin receptor–like kinase 2 (ALK-2). GAPDH was used as a loading control for protein content. B, Ratio of p-Smad1 to total Smad1 in chondrocytes from WT mice (solid bars) and CD44−/− mice (hatched bars), as indicated by the pixel intensities of the quantified protein bands for each experimental condition. Values are the mean ± SD of 5 separate experiments. * = P < 0.05. C, Bovine articular chondrocytes (BACs) from 18–24-month-old adult steers were pretreated with hyaluronidase, stimulated with BMP-7, and analyzed by Western blotting for p-Smad1, total Smad, and ALK-2. GAPDH was used as a loading control for protein content. Results are representative of 2 independent experiments. These results demonstrate that hyaluronan is required for optimal BMP-7 responsiveness in chondrocytes from WT mice, CD44−/− mice, and steers. Additionally, no changes in BMP receptor ALK-2 were observed.