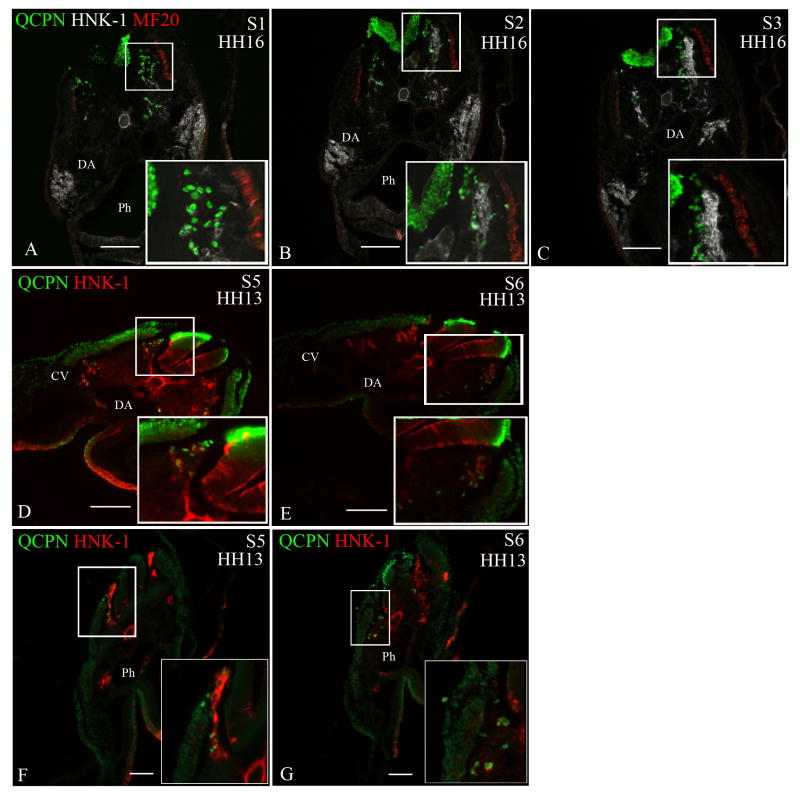
Figure 4. Neural crest cells from the level of somites 1-3 [stage-10 embryos] exhibit migratory plasticity.
Quail neural tubes (labeled with QCPN antibody; green) from somite-level 1-3 were heterotopically or heterochronically transplanted into a stage-10 chicken embryo to test for cell autonomous behavior. Neural crest cells are labeled with HNK-1 antibody (red) and the myotome labeled with MF20 (white A-C only) to indicate unambiguously the boundary between the dorsolateral and ventral pathways. The boxed areas are shown at higher magnification in the insets. Representative sections are shown from somite-levels 1,2,3, (A-C) or somite levels 5 and 6 (D,E; F-G).
When a quail neural tube from the level of somites 1-3 [stage 10] is isotopically transplanted into a stage-13 chick embryo host (A-C) or heterotopically transplanted to the level of somites 5-7 in a stage-10 chick host (D-E), the transplanted neural crest cells (QCPN-positive) switch their migration to the ventral pathway, 12 hours later [stage 16 and 13, respectively], thus mimicking the migratory behavior of the endogenous neural crest. (F-G) The ventrally-migrating neural crest cells from the level of somites 1-3 [stage 13] migrate in the ventral pathway when transplanted to the level of somites 5-7 in stage-10 embryo hosts, 12 hours later [stage 13] like the endogenous cells.
Somite 1 (S1), Somite 2 (S2), Somite 3 (S3), Somite 5 (S5), Somite 6 (S6), Dermomyotome (DM), Dorsal aorta (DA), Neural tube (NT), Pharynx (Ph). Scale bar = 100μm.