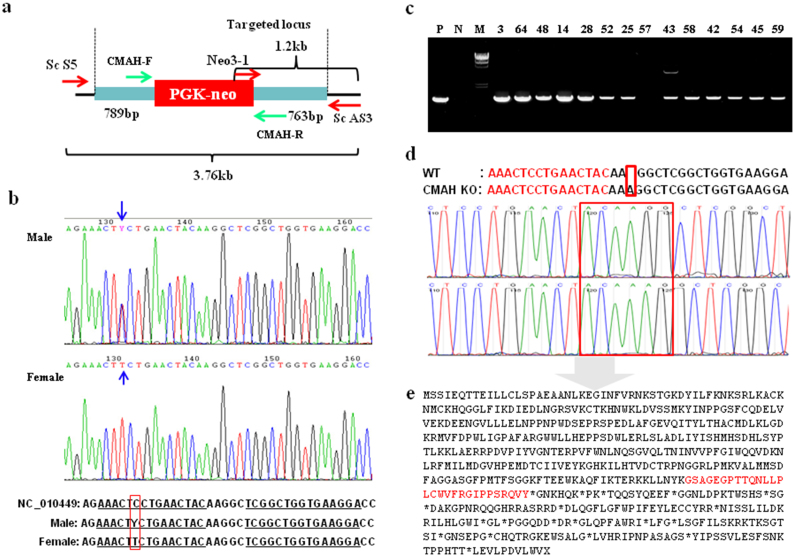
Figure 3. Selection of CMAH targeted cells using a selection-independent and -dependent zinc finger nucleases.
(a) Design of the donor DNA and primers used for this study. The locations of primers used for genotyping are shown in the figure. (b) SNP heterozygosity of the ZFN binding site on the CMAH gene. Sequencing PCR products include the ZFN cutting site show that there is a SNP within the ZFN binding site (arrow). Female show complete mismatch compared to the reference sequence of pig CMAH (NC_010449). The position of the DNA nucleotide mutation is indicated by the red box. (c) Screening of KO events by PCR. 1.2 kb PCR product using primers of Neo 3-1 and ScAS3 indicates a KO event. PCR products (1.2 kb) indicate the amplification of right HR junction using Neo3-1 and ScAS3 primer. M, size marker (λ/HindIII and 1 kb ladder); P, positive control; N, negative control; Number, G418-resistant colonies. (d) Mutagenesis generated by ZFN. Sequencing PCR products includes ZFN cutting site show that ZFN alone could generate mutations adjacent to ZFN cutting sites. An insertion of adenosine on the left side of the ZFN cutting site was observed. (e) Predicted amino acid sequence of CMAH from disrupted allele in KO pigs by NHEJ. Premature stop codon (*) is generated by NHEJ and series of amino acid sequence before the stop codon does not code for any known protein. Red letters indicate newly generated amino acids due to the frame shift.