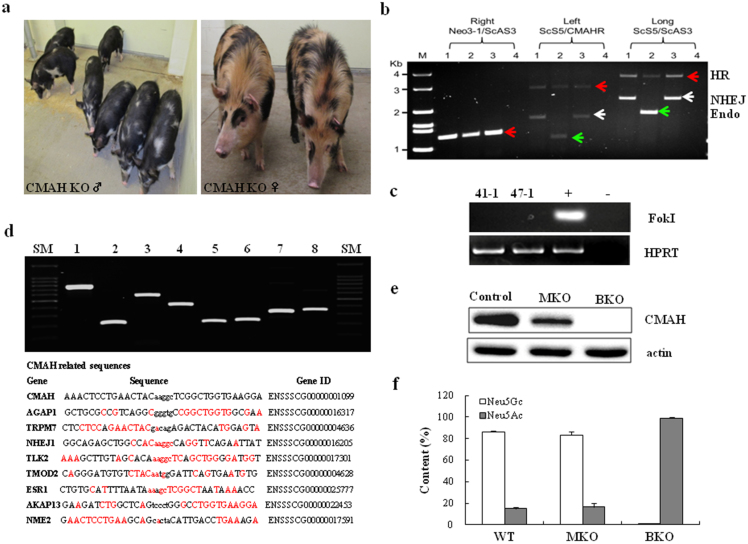
Figure 4.
(a) Images of CMAH KO pigs. (b) Genotyping of CMAH KO pigs. For genotyping, three different PCRs were run to verify KO events. Right indicates the amplification of right HR junction using Neo3-1 and ScAS3 primers. Left shows the amplification of left HR junction (1.2 kb for endogenous and 3.2 kb for KO by HR). Long is the the amplification of entire HR junction (1.8 kb for endogenous and 3.7 kb for KO by HR). PCR products from biallelic KO pigs suggest that one allele has 1 bp insertion through complete HR and the other allele has an insertion of 500 bp on the locus: lane 1 and 3: pigs from female D1 (biallelic KO); lane 2: a pig from B2 (heterozygous); lane 4: negative control. HR (red arrow), NHEZ (white arrow), and Endo (green arrow) indicate amplified DNA by homologous recombination, non-homologous end joints, and endogenous DNA, respectively. (c) PCR amplification of FokI domain from genemic DNAs of CMAH KO pigs [41-1 and 47-1 are DNAs from male and female pigs shown in (a)]. HPRT gene was used as an internal control. (d) Upper) Cel-I digest of heteroduplex DNA revealed no additional off-target mutations at the 8 loci with highest homology to CMAH; lane 1, AGAP1; 2, TRPM7; 3, NJEJ1; 4, TLK2; 5, TMOD2; 6, ESR1; 7, AKAP13; 8, NME2, SM, size marker. Bottom) Genes, gene IDS, and sequence homologies of CMAH related sequence to exclude off-target mutations. Upper case: ZFN binding sites; lower case; ZFN cut site; homolog base pairs in red. SM indicates size markers. (e) Western blot analysis: expression of CMAH gene in the fibroblast cells from wild type, CMAH monoallelic (MKO) and biallelic (BKO) mutant minature pigs; Actin was used as a housekeeping protein. (f) Comparison of Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc contents between control and KO pigs. The Neu5Gc content was determined based on the signal intensities (peak areas from Supplementary Fig. 2) of each 1,2-diamino-4, 5-methylenedioxybenzene (DMB) fluorescence–labeled Neu5Gc and Neu5Ac. Each value is the mean ± SD of triplicate determinations and was confirmed by t-test.