Figure 9.
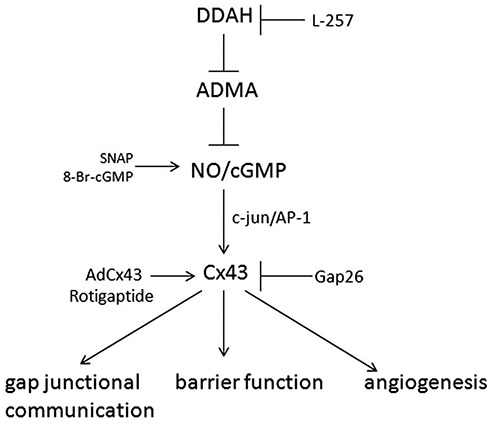
Proposed role of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)/dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase I (DDAHI) in the regulation of pulmonary endothelial function. ADMA inhibits nitric oxide (NO)–cGMP signaling, leading to a decrease in c-jun expression and phosphorylation, connexin 43 (Cx43) expression, and gap junctional communication. Loss of Cx43 destabilizes intercellular junctions, contributing to the breakdown of endothelial barrier function and inhibition of angiogenesis. The DDAHI-selective inhibitor L-257 and Cx43 inhibitor Gap 26 mimic the effects of ADMA, while overexpression of DDAHI, Cx43, or treatment with rotigaptide has a protective effect. SNAP: S-nitroso-N-acetyl-d, l-penicillamine; NO: nitric oxide; cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate; AP-1: activator protein 1.
