Figure 3.
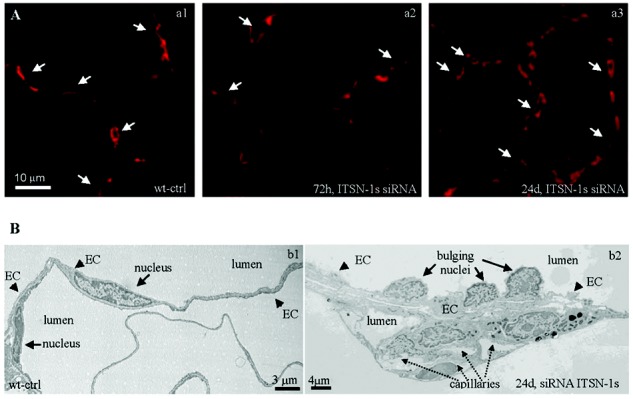
Chronic intersectin-1s knockdown (KDITSN-1s) in mouse lungs induces microvascular remodeling. A, Micrographs of GS-1 lectin staining of paraffin-embedded sections show microvessel profiles (arrows) within the alveolar walls in wild-type control (wt-ctrl) mice (a1), mice treated with small interfering RNA (siRNAITSN) for 3 days (a2), and mice treated with siRNAITSN for 24 days (a3). Scale bar: 10 μm. B, Ultrastructural features of microvascular remodeling in KDITSN mouse lungs (24 days). b1, Two vessel profiles in wt-ctrl mouse lungs display elongated endothelial cell (EC) nuclei. Note the relatively uniform thickness of the ECs throughout the vessel perimeter. b2, Segment of a midsized vessel in KDITSN mouse lung shows a distorted endothelium and several nuclei protruding into the lumen (arrows). New pulmonary microvessels (dashed arrows) with narrow openings are abundant and located in very close proximity to each other.
