Figure 9. Proposed model of cohesin architecture and Pds5 function.
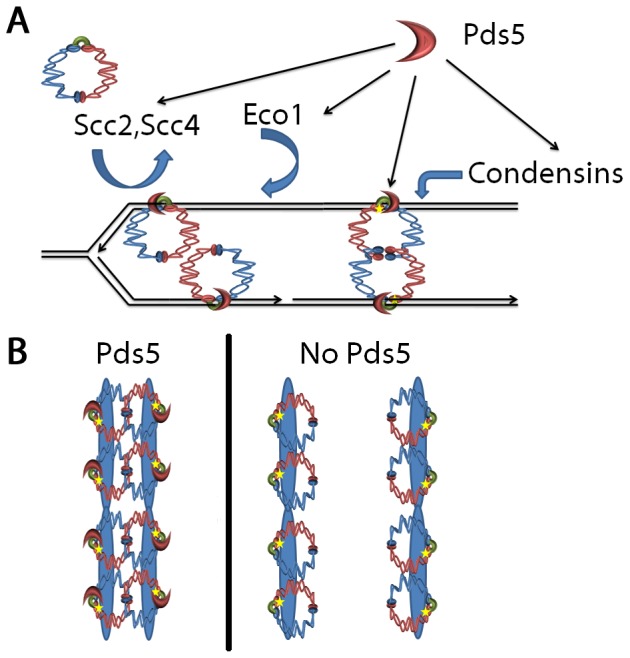
(A) Scc2,Scc4-dependent cohesin loading during S-phase onto nascent sister chromatids is coordinated with Eco1-dependent Smc3 acetylation, leading to stable cohesin-cohesin interactions. Many cohesin structures are possible; shown is one model that reflects recent advances in SMC-like crystal structure studies through which chromatin is captured between SMC head domains and an Mcd1 cap complex [1]. Note the role of Pds5 and Eco1-dependent Smc3 acetylation in regulating hinge-hinge interactions and additional roles for Pds5 in establishing condensation and transcription regulation (not shown). (B) Summary of results that, upon Pds5 inactivation during mitosis, sister chromatid cohesion is lost despite retention of cohesin to DNA and Smc3 acetylation.
