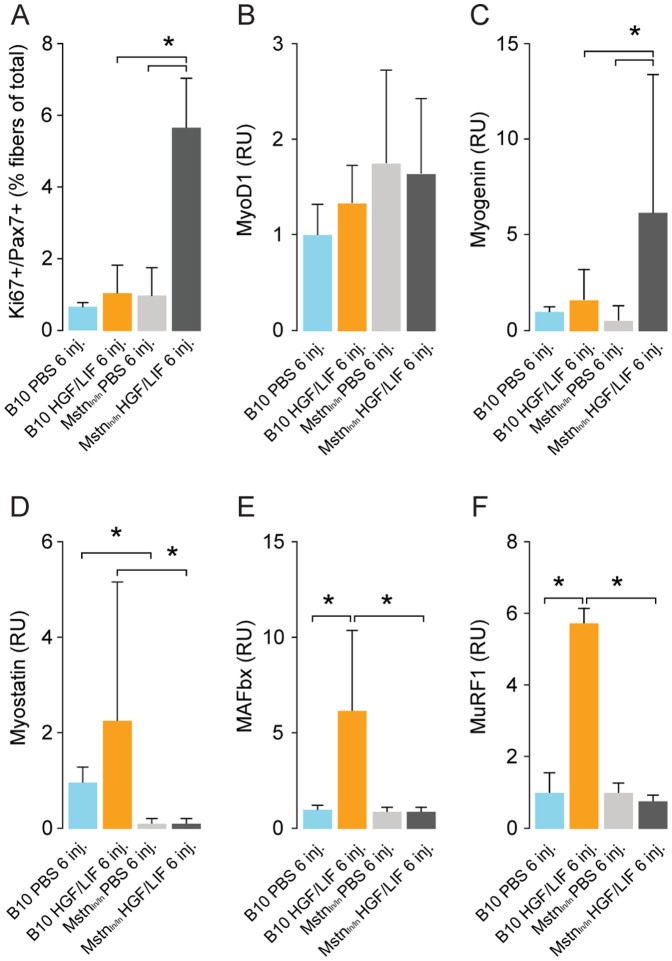
Figure 10. Alternating hepatocyte growth factor and leukemia inhibitory factor treatment increases satellite cells undergoing mitotic divisions and decreases mRNA expression levels of protein breakdown pathway components in normoxic myostatin deficient mice.
Tibialis anterior sections were incubated with antibodies specific for satellite cell marker Pax7, proliferation marker Ki67. Alternating injections of normoxic B10 mice with hepatocyte growth factor and leukemia inhibitory factor (N = 8, yellow) did not change ratio of satellite cells undergoing mitotic divisions compared to PBS injected B10 mice (N = 8, light blue) (A). Ratio of satellite cells undergoing mitotic divisions was significantly increased in normoxic Mstnln/ln mice after repeated alternating injections with HGF/LIF (N = 8, dark grey) compared to PBS injected Mstnln/ln mice (N = 8, light grey). RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA expression levels yielded no difference in levels of MyoD was observed between groups (B). Alternating injections of normoxic Mstnln/ln mice with hepatocyte growth factor and leukemia inhibitory factor lead to increased levels of myogenin and decreased levels of myostatin, MAFbx and MuRF1 compared to treated normoxic B10 mice (B-F). RU = Relative Units. Error bars are SD; One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc correction for multiple comparisons was used to assess differences among groups for each dependent variable. *denotes significant (P<0.05). Data are representative of one independent experiment (A) and four independent experiments (B-F).