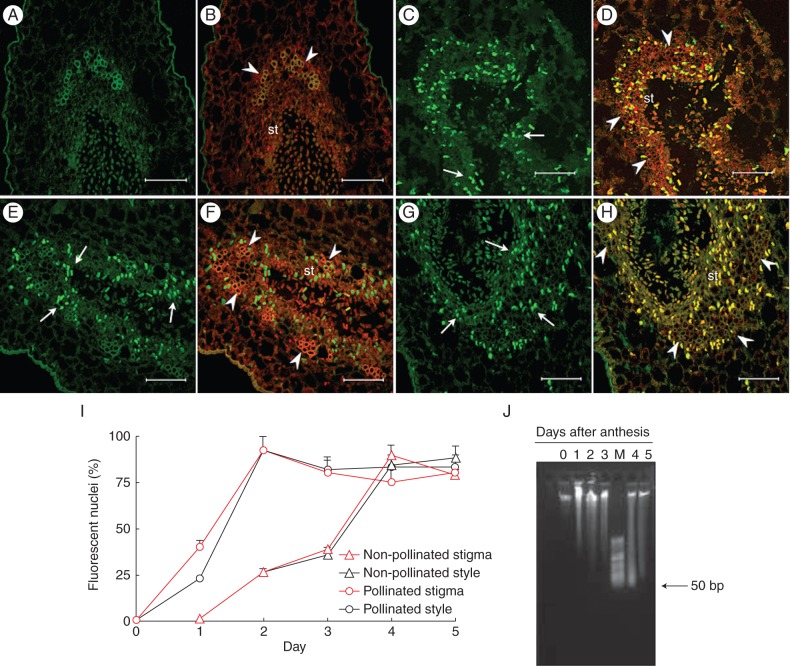
Fig. 4.
In situ detection of nuclear DNA fragmentation in sections of kiwifruit stigmatic arms by TUNEL assay (A, C, E, G) and counterstained with propidium iodide (B, D, F, H). (A–D) Non-pollinated stigmatic arms sectioned at the level of the stigma showing no nuclei with a positive TUNEL reaction on the first day after anthesis in (A, B), but reaching the maximum number of TUNEL-positive nuclei (arrow) on the fourth day in (C, D). (E–H) Pollinated stigmatic arms sectioned at the level of the stigma showing TUNEL-positive nuclei (arrow) from the first day after anthesis in (E, F), and reaching the maximum number of reactive nuclei on the second day in (G, H). (I) Percentage of TUNEL-reactive nuclei in sections at the levels of the stigma and the base of style from non-pollinated and pollinated flowers. Data represent the percentage (mean ± s.e.) of TUNEL-reactive nuclei from a total of 100 nuclei stained with propidium iodide and counted in at least two stigmatic arms per day and per treatment. (J) Agarose (0·8 %) gel electrophoresis of total DNA isolated from the stigmatic arms of pollinated kiwifruit flowers collected from 0 to 5 d after anthesis. Scale bars (A–H) = 75 μm. Abbreviations: st, secretory tissue; M, HyperLadder II DNA molecular marker of low molecular weight (50–2000 bp). Arrowheads indicate vascular tissue in (B, D, F, H).