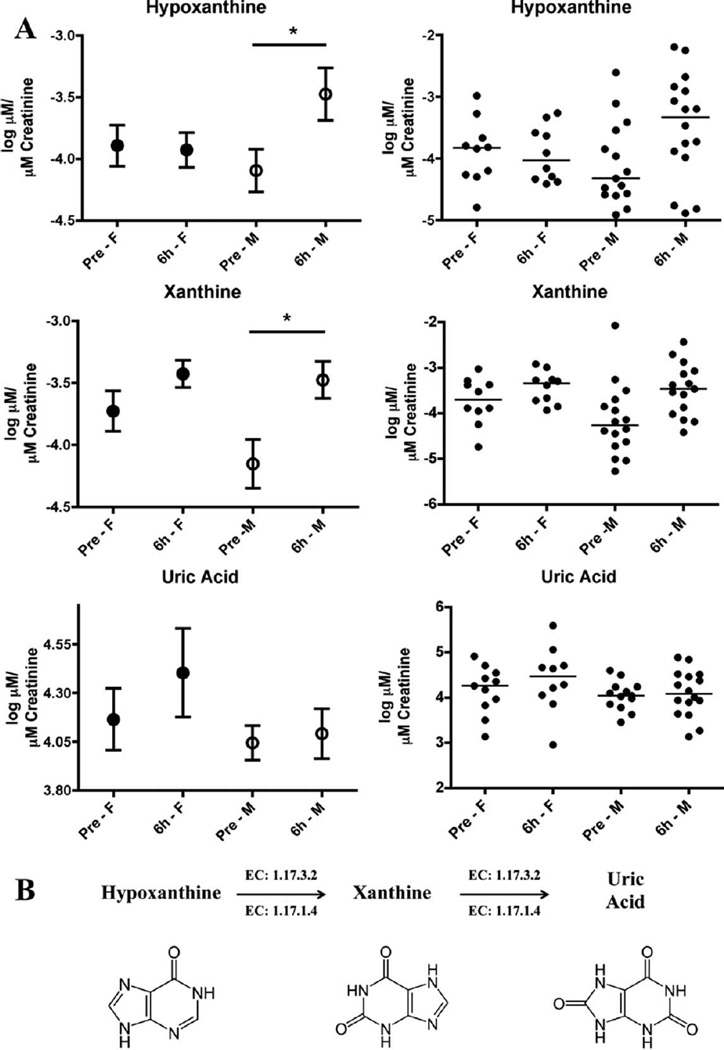
FIG. 3.
Quantification of hypoxanthine, xanthine and uric acid. All three metabolites are part of the purine catabolism, as indicated in the enzymatic pathway (xanthine oxidase: 1.17.3.2, xanthine dehydrogenase: 1.17.1.4). Uric acid is the last step of the pathway in humans. Results on the left hand panels are presented as mean of log (µM of metabolite/µM excreted creatinine) ± SEM, and plotted on the right panels is the distribution in the population with lines signifying the median. The pre-exposure and 6 h post-exposure groups were further analyzed based on sex, revealing that the purine catabolism is highly responsive in the adult male population, whereas adult females only exhibit trends of upregulated excretion. The assumption of statistical normality was confirmed for all features by the Anderson-Darling test at the 10% significance level. Asterisks represent a P value of <0.05, according to the t test with Welch’s correction.