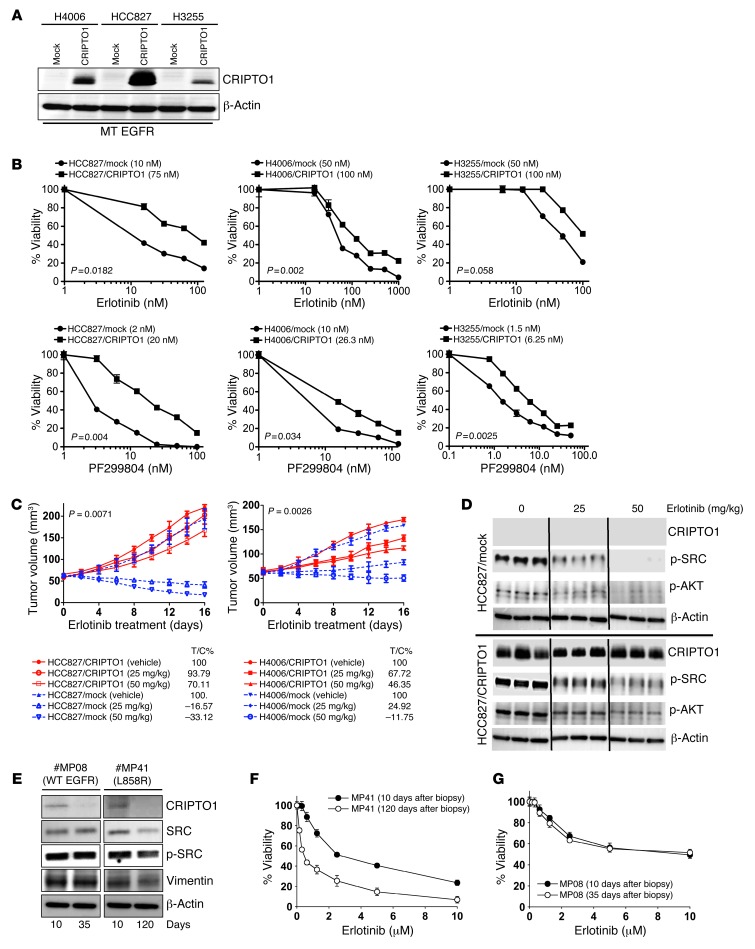
Figure 2. CRIPTO1 renders EGFR-mutated NSCLC cells resistant to EGFR-TKIs in vitro, in vivo, and in primary cultures.
(A) Western blot of CRIPTO1 in CRIPTO1-transfected NSCLC cells. MT, mutant. Exogenous CRIPTO1 expression in HCC827/CRIPTO1 cells is the highest among the 3 transfected cell lines and comparable to that in NSCLC samples (Figure 1A), indicating that exogenous CRIPTO1 expression in all the 3 CRIPTO1-transfected cells should be similar to that in the NSCLC samples. (B) Effect of CRIPTO1 on erlotinib and dacomitinib sensitivity of EGFR-mutant NSCLC cells. MTS assays were performed 72 hours after drug treatment. Data represent mean ± SD of triplicate measurements relative to untreated cells. P values were calculated using paired 2-tailed t test. IC50s are reported in parenthesis in graphs. (C) Effect of CRIPTO1 expression on erlotinib sensitivity of HCC827 and H4006 cells in vivo. See Methods for details. P values were significant between vehicle and all the treatment groups (ANOVA). Bars indicate SEM. (D) Western blot of CRIPTO1, pSRC, and pAKT in xenograft tumors. Tumor cells were harvested at day 16 after erlotinib treatment. Lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous. (E) Progressive loss of CRIPTO1 expression during in vitro culture of human primary NSCLC cells. Western blot of CRIPTO1 of primary cells derived from an intrinsic erlotinib-resistant NSCLC patient carrying L858R EGFR (MP41) and an NSCLC patient carrying WT EGFR (MP08) at the indicated days of primary culture. (F and G) Correlation between progressive loss of CRIPTO1 expression and erlotinib sensitivity in MP08 and MP41 cells.